direct synthesis of hydrogen peroxide from oxygen and hydrogen
... consideration of both quantity and quality (hazard) of chemicals involved in the synthesis of a chemical product. This new metric was used to evaluate the greenness of various synthetic methods in this study. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a widely used green oxidant, is currently produced by an anthraqu ...
... consideration of both quantity and quality (hazard) of chemicals involved in the synthesis of a chemical product. This new metric was used to evaluate the greenness of various synthetic methods in this study. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a widely used green oxidant, is currently produced by an anthraqu ...
Ch. 6 - Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Professor William Tam received his B.Sc. at the University of Hong Kong in 1990 and his Ph.D. at the University of Toronto (Canada) in 1995. He was an NSERC postdoctoral fellow at the Imperial College (UK) and at Harvard University (USA). He joined the Department of Chemistry at the University of Gu ...
... Professor William Tam received his B.Sc. at the University of Hong Kong in 1990 and his Ph.D. at the University of Toronto (Canada) in 1995. He was an NSERC postdoctoral fellow at the Imperial College (UK) and at Harvard University (USA). He joined the Department of Chemistry at the University of Gu ...
aa-2005-38-71-negishi - University of Windsor
... the multimechanistic and multifaceted nature of the Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling, however, it is not practical to compare and rank them on one scale. From a practical viewpoint, synthetic chemists are generally seeking those methods and reactions that satisfy some or most, if not all, of the followin ...
... the multimechanistic and multifaceted nature of the Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling, however, it is not practical to compare and rank them on one scale. From a practical viewpoint, synthetic chemists are generally seeking those methods and reactions that satisfy some or most, if not all, of the followin ...
C−C, C−O, C−N Bond Formation on sp2 Carbon by Pd(II)
... Carbon-carbon bond formation taking place when C-H units are functionalized through the action of palladium complexes is one of the most important subjects of contemporary chemistry; its use appears particularly striking when the metal complex is active in a catalytic amount. The aim of this section ...
... Carbon-carbon bond formation taking place when C-H units are functionalized through the action of palladium complexes is one of the most important subjects of contemporary chemistry; its use appears particularly striking when the metal complex is active in a catalytic amount. The aim of this section ...
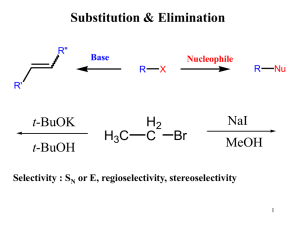
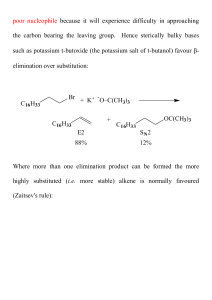
Elimination Reactions
... neutral conditions with polar solvents, such as water, ethyl alcohol or acetic acid. • E1 reactions can also occur with strong bases, but only at low concentration, about 0.01 to 0.1 M or below. • E2 reactions require strong base in high concentration, about 1 M or above. ...
... neutral conditions with polar solvents, such as water, ethyl alcohol or acetic acid. • E1 reactions can also occur with strong bases, but only at low concentration, about 0.01 to 0.1 M or below. • E2 reactions require strong base in high concentration, about 1 M or above. ...
Cracking (chemistry)

In petroleum geology and chemistry, cracking is the process whereby complex organic molecules such as kerogens or heavy hydrocarbons are broken down into simpler molecules such as light hydrocarbons, by the breaking of carbon-carbon bonds in the precursors. The rate of cracking and the end products are strongly dependent on the temperature and presence of catalysts. Cracking is the breakdown of a large alkane into smaller, more useful alkanes and alkenes. Simply put, hydrocarbon cracking is the process of breaking a long-chain of hydrocarbons into short ones. More loosely, outside the field of petroleum chemistry, the term ""cracking"" is used to describe any type of splitting of molecules under the influence of heat, catalysts and solvents, such as in processes of destructive distillation or pyrolysis. Fluid catalytic cracking produces a high yield of petrol and LPG, while hydrocracking is a major source of jet fuel, Diesel fuel, naphtha, and again yields LPG.