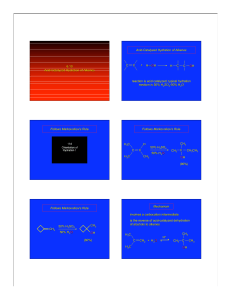
technical bulletin reaction solvent dimethyl sulfoxide (dmso)
... DMSO is a versatile and powerful solvent that will dissolve most aromatic and unsaturated hydrocarbons, organic nitrogen compounds, organo-sulfur compounds and many inorganic salts. It is miscible with most of the common organic solvents such as alcohols, esters, ketones, lower ethers, chlorinated s ...
... DMSO is a versatile and powerful solvent that will dissolve most aromatic and unsaturated hydrocarbons, organic nitrogen compounds, organo-sulfur compounds and many inorganic salts. It is miscible with most of the common organic solvents such as alcohols, esters, ketones, lower ethers, chlorinated s ...
Sample
... HBr to alkenes in 1869. Markovnikov stated : MARKOVNIKOV'S RULE : The addition of a proton acid to the double bond of an alkene result in a product with the acid proton bonded to the carbon atom that already holds the greater number of hydrogen atoms. This is the original statement of Markovnikov's ...
... HBr to alkenes in 1869. Markovnikov stated : MARKOVNIKOV'S RULE : The addition of a proton acid to the double bond of an alkene result in a product with the acid proton bonded to the carbon atom that already holds the greater number of hydrogen atoms. This is the original statement of Markovnikov's ...
What is Organic Chemistry?
... Organic chemistry is essential to the understanding of the intricate details of life The interactions and reactions of organic molecules are what define living systems. One needs to understand bonding, structure, properties, reactions, and synthesis to understand natural systems. CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCT ...
... Organic chemistry is essential to the understanding of the intricate details of life The interactions and reactions of organic molecules are what define living systems. One needs to understand bonding, structure, properties, reactions, and synthesis to understand natural systems. CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCT ...
Alcohols, Ethers, and Epoxides
... In Chapter 9, we take the principles learned in Chapters 7 and 8 about leaving groups, nucleophiles, and bases, and apply them to alcohols, ethers, and epoxides, three new functional groups that contain polar C – O bonds. In the process, you will discover that all of the reactions in Chapter 9 follo ...
... In Chapter 9, we take the principles learned in Chapters 7 and 8 about leaving groups, nucleophiles, and bases, and apply them to alcohols, ethers, and epoxides, three new functional groups that contain polar C – O bonds. In the process, you will discover that all of the reactions in Chapter 9 follo ...
Soot Formation Modeling during Hydrocarbon
... reactions of neutral species were not fast enough and suggested an ionic mechanism. In the model chemi-ions are assumed to be the precursors of soot on which free radicals, polyacetylenes, and PAH repeatedly add through fast ion-molecule reactions. Calcote claimed that H3 O+ was the dominant ion in ...
... reactions of neutral species were not fast enough and suggested an ionic mechanism. In the model chemi-ions are assumed to be the precursors of soot on which free radicals, polyacetylenes, and PAH repeatedly add through fast ion-molecule reactions. Calcote claimed that H3 O+ was the dominant ion in ...
OC 2/e Ch 11
... sulfides: treat one mole of Na2S with two moles of an alkyl halide RSR + 2 N aX ...
... sulfides: treat one mole of Na2S with two moles of an alkyl halide RSR + 2 N aX ...
PowerPoint - Naming Hydrocarbons
... – Alkenes: An alkene has at least one double bond. It will have 2 less hydrogens (than a comparable alkane) for each double bond. – Alkynes: An alkyne has at least one triple bond. It will have 4 less hydrogens (than a comparable alkane) for each triple bond. ...
... – Alkenes: An alkene has at least one double bond. It will have 2 less hydrogens (than a comparable alkane) for each double bond. – Alkynes: An alkyne has at least one triple bond. It will have 4 less hydrogens (than a comparable alkane) for each triple bond. ...
The Reactions of Osmium(VIII) in Hydroxide
... t = 986 minutes, upon addition of 1.00 × 10 mol/L methanol. The spectra denoted by A, B, and C respectively refer to the spectra recorded at t = 0, t = 34 and t = 986 minutes. The solid arrow indicates the direction of absorbance change with time. The solid and dashed lines indicate the occurrence o ...
... t = 986 minutes, upon addition of 1.00 × 10 mol/L methanol. The spectra denoted by A, B, and C respectively refer to the spectra recorded at t = 0, t = 34 and t = 986 minutes. The solid arrow indicates the direction of absorbance change with time. The solid and dashed lines indicate the occurrence o ...
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes
... transition state for attack of water on bromonium ion has carbocation character; more stable transition state (left) has positive charge on more highly substituted carbon ...
... transition state for attack of water on bromonium ion has carbocation character; more stable transition state (left) has positive charge on more highly substituted carbon ...
Chapter 6 Addition Reactions to Alkenes
... As we have seen, according the Markovnikov’s rule, the electrophile adds to the less substituted carbon so as to allow the positive charge to be supported at the more substituted and therefore more electron rich carbon. In the present case, the addition of the electrophile (the boron) and the nucleo ...
... As we have seen, according the Markovnikov’s rule, the electrophile adds to the less substituted carbon so as to allow the positive charge to be supported at the more substituted and therefore more electron rich carbon. In the present case, the addition of the electrophile (the boron) and the nucleo ...
Organic – Nomenclature – III
... of the parent compounds. Note that ene and yne functions belonging to type B groups appear always as co-suffixes with the highest priority group in the parent name. This thing will be clarified with a lot of examples later. PRIORITY ORDER AMONG TYPE (C) FUNCTIONAL GROUPS The following table gives th ...
... of the parent compounds. Note that ene and yne functions belonging to type B groups appear always as co-suffixes with the highest priority group in the parent name. This thing will be clarified with a lot of examples later. PRIORITY ORDER AMONG TYPE (C) FUNCTIONAL GROUPS The following table gives th ...
Haloalkanes-haloarenes
... 10.Melting point of p-dibromobenzene is higher than its o- & m- isomers. A. Due to the symmetry of its structure, p-isomer fits better in the crystal lattice. 11. Free radical halogenation of alkanes is not preferred for the preparation of haloalkanes. A. This method gives a complex mixture of isome ...
... 10.Melting point of p-dibromobenzene is higher than its o- & m- isomers. A. Due to the symmetry of its structure, p-isomer fits better in the crystal lattice. 11. Free radical halogenation of alkanes is not preferred for the preparation of haloalkanes. A. This method gives a complex mixture of isome ...
an introduction to organic reactions
... primarily as the bane of existence of premeds and science majors. ...
... primarily as the bane of existence of premeds and science majors. ...
Organic Chemistry introduction
... MP Branching reduces the flexibility of the molecule which reduces the entropy term S in the equation Tmp = H/S. Since S is in the denominator, Tmp increases. BP Branching reduces surface area (more compact structure), and therefore London dispersion forces which control boiling point for these ...
... MP Branching reduces the flexibility of the molecule which reduces the entropy term S in the equation Tmp = H/S. Since S is in the denominator, Tmp increases. BP Branching reduces surface area (more compact structure), and therefore London dispersion forces which control boiling point for these ...
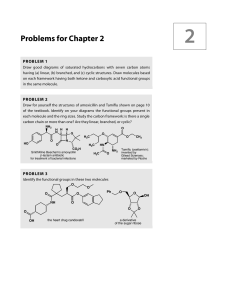
Problems for Chapter 2
... below. How many DBEs (double bond equivalents—see p. 75 in the textbook) are there in C4H6O2? What are the structures of the four compounds? You might again find it useful to draw a few structures to start with. (a) IR: 1745 cm–1; 13C NMR 214, 82, 58, and 41 ppm (b) IR: 3300 cm–1 (broad); 13C NMR 62 ...
... below. How many DBEs (double bond equivalents—see p. 75 in the textbook) are there in C4H6O2? What are the structures of the four compounds? You might again find it useful to draw a few structures to start with. (a) IR: 1745 cm–1; 13C NMR 214, 82, 58, and 41 ppm (b) IR: 3300 cm–1 (broad); 13C NMR 62 ...
Organic Chemistry
... Because of the relative stability of alkyl radical intermediates, selectivity in free radical halogenation favors tertiary over secondary over primary carbon radicals. Bromination, though, is more selective than chlorination, because the proton extraction step is more endothermic in bromination than ...
... Because of the relative stability of alkyl radical intermediates, selectivity in free radical halogenation favors tertiary over secondary over primary carbon radicals. Bromination, though, is more selective than chlorination, because the proton extraction step is more endothermic in bromination than ...
barker_rg
... Trimellitic-anhydride (the 1,2-anhydride of 1,2,4-tricarboxy benzene), hereafter referred to as TMA, contains both an aromatic acid group and a cyclic anhydride group. ...
... Trimellitic-anhydride (the 1,2-anhydride of 1,2,4-tricarboxy benzene), hereafter referred to as TMA, contains both an aromatic acid group and a cyclic anhydride group. ...
THE FRIEDEL-CRAFTS BENZYLATION OF ARENES AND THE
... unbiased arenes with unactivated C–H bonds. However, the harsh reaction conditions, the generation of stoichiometric metal waste (e.g. aluminum) and the poor reactivity with electron-poor substrates dramatically limit the use of Friedel-Crafts processes. We wanted to address these limitations and de ...
... unbiased arenes with unactivated C–H bonds. However, the harsh reaction conditions, the generation of stoichiometric metal waste (e.g. aluminum) and the poor reactivity with electron-poor substrates dramatically limit the use of Friedel-Crafts processes. We wanted to address these limitations and de ...
The Results from a Canadian National Field Trial Comparing 1,8-
... The differences observed between the Israeli and UK research groups regarding 1,2-indanedione formulations and development conditions highlight the need to perform regional field trials in order to be confident that the solutions recommended in Canada are truly the best for that region of the countr ...
... The differences observed between the Israeli and UK research groups regarding 1,2-indanedione formulations and development conditions highlight the need to perform regional field trials in order to be confident that the solutions recommended in Canada are truly the best for that region of the countr ...
Aldehydes and ketones
... 1. Oxidation – Tollens Test - Benedicts Test 2. Reduction – Hydrogen addition – NaBH4 reagent 3. Addition of Alcohols – hemiacetal/acetal and tautomerism ...
... 1. Oxidation – Tollens Test - Benedicts Test 2. Reduction – Hydrogen addition – NaBH4 reagent 3. Addition of Alcohols – hemiacetal/acetal and tautomerism ...
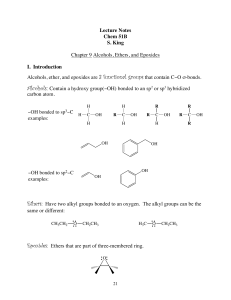
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 9 Alcohols, Ethers, and
... acidic conditions, both 2° & 3° alcohols undergo an E1 reaction, whereas 1° alcohols go undergo an E2 reaction. All three (1°, 2° and 3°) have the same first step, protonation of the hydroxyl group by the strong acid to make it a better LG: ...
... acidic conditions, both 2° & 3° alcohols undergo an E1 reaction, whereas 1° alcohols go undergo an E2 reaction. All three (1°, 2° and 3°) have the same first step, protonation of the hydroxyl group by the strong acid to make it a better LG: ...
Organic Chemistry: Introduction
... – bonds are omitted, repeated groups put together, side chains put in brackets • CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 –or even CH3(CH2)4CH3 • CH3CH(CH3)CH3 (this is not the molecule above) ...
... – bonds are omitted, repeated groups put together, side chains put in brackets • CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 –or even CH3(CH2)4CH3 • CH3CH(CH3)CH3 (this is not the molecule above) ...
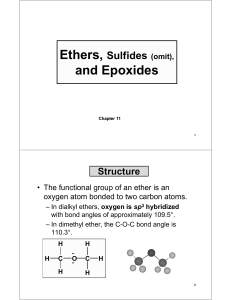
(omit), and Epoxides
... • IUPAC: the longest carbon chain is the parent. Name the OR group as an alkoxy substituent. • Common names: name the groups bonded to oxygen in alphabetical order followed by the word ether. OH ...
... • IUPAC: the longest carbon chain is the parent. Name the OR group as an alkoxy substituent. • Common names: name the groups bonded to oxygen in alphabetical order followed by the word ether. OH ...
Topic 10.1 Fundametals of Organic Chemistry
... used in questions – every “corner” represents a carbon – hydrogens are implied ...
... used in questions – every “corner” represents a carbon – hydrogens are implied ...
Ene reaction

The ene reaction (also known as the Alder-ene reaction) is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen (the ene) and a compound containing a multiple bond (the enophile), in order to form a new σ-bond with migration of the ene double bond and 1,5 hydrogen shift. The product is a substituted alkene with the double bond shifted to the allylic position.This transformation is a group transfer pericyclic reaction, and therefore, usually requires highly activated substrates and/or high temperatures. Nonetheless, the reaction is compatible with a wide variety of functional groups that can be appended to the ene and enophile moieties. Also,many useful Lewis acid-catalyzed ene reactions have been developed which can afford high yields and selectivities at significantly lower temperatures, making the ene reaction a useful C–C forming tool for the synthesis of complex molecules and natural products.