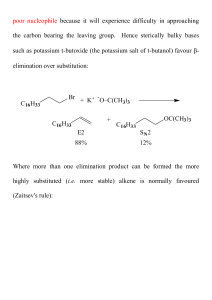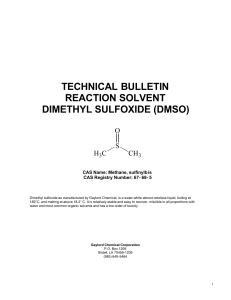
technical bulletin reaction solvent dimethyl sulfoxide (dmso)
... DMSO is a versatile and powerful solvent that will dissolve most aromatic and unsaturated hydrocarbons, organic nitrogen compounds, organo-sulfur compounds and many inorganic salts. It is miscible with most of the common organic solvents such as alcohols, esters, ketones, lower ethers, chlorinated s ...
... DMSO is a versatile and powerful solvent that will dissolve most aromatic and unsaturated hydrocarbons, organic nitrogen compounds, organo-sulfur compounds and many inorganic salts. It is miscible with most of the common organic solvents such as alcohols, esters, ketones, lower ethers, chlorinated s ...
Alkenes 4 - ChemWeb (UCC)
... In the transition state for the SN2 attack of a nucleophile on a cyclic mercurinium or bromonium cation bond-breaking of the C-Hg or C-Br bond is more advanced than bond-formation with the incoming nucleophile. Hence the SN2 transition state for this reaction has partial carbocationic (i.e. SN1) cha ...
... In the transition state for the SN2 attack of a nucleophile on a cyclic mercurinium or bromonium cation bond-breaking of the C-Hg or C-Br bond is more advanced than bond-formation with the incoming nucleophile. Hence the SN2 transition state for this reaction has partial carbocationic (i.e. SN1) cha ...
barker_rg
... Trimellitic-anhydride (the 1,2-anhydride of 1,2,4-tricarboxy benzene), hereafter referred to as TMA, contains both an aromatic acid group and a cyclic anhydride group. ...
... Trimellitic-anhydride (the 1,2-anhydride of 1,2,4-tricarboxy benzene), hereafter referred to as TMA, contains both an aromatic acid group and a cyclic anhydride group. ...
THE FRIEDEL-CRAFTS BENZYLATION OF ARENES AND THE
... First, I would like to thank my supervisor Prof. Dr. Jeffrey W. Bode for giving me the opportunity to work in his research group. After the group arrived from UPenn, I was one of his first new PhD students at ETH and I feel really fortunate that I could join the group during this exciting time. Jeff ...
... First, I would like to thank my supervisor Prof. Dr. Jeffrey W. Bode for giving me the opportunity to work in his research group. After the group arrived from UPenn, I was one of his first new PhD students at ETH and I feel really fortunate that I could join the group during this exciting time. Jeff ...
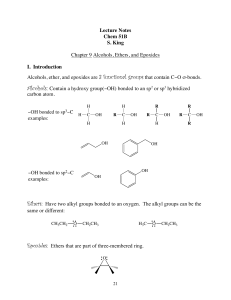
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 9 Alcohols, Ethers, and
... The mechanism depends on the structure of the alcohol. Under these strongly acidic conditions, both 2° & 3° alcohols undergo an E1 reaction, whereas 1° alcohols go undergo an E2 reaction. All three (1°, 2° and 3°) have the same first step, protonation of the hydroxyl group by the strong acid to make ...
... The mechanism depends on the structure of the alcohol. Under these strongly acidic conditions, both 2° & 3° alcohols undergo an E1 reaction, whereas 1° alcohols go undergo an E2 reaction. All three (1°, 2° and 3°) have the same first step, protonation of the hydroxyl group by the strong acid to make ...
Lorell Thesis Final Version in PDF S
... Figure 22. 13C and 1H NMR of syn-(S,S)-90d. ........................................................ 68 Figure 23. 31P NMR of CDA derivative of 90d. ........................................................ 69 Figure 24. 13C and 1H NMR of syn-(R,R)-90e. ............................................... ...
... Figure 22. 13C and 1H NMR of syn-(S,S)-90d. ........................................................ 68 Figure 23. 31P NMR of CDA derivative of 90d. ........................................................ 69 Figure 24. 13C and 1H NMR of syn-(R,R)-90e. ............................................... ...
New Stereoselective Approaches to Highly Substituted
... using a mixture o f sodium iodide and m-chloroperbenzoic acid (mCPBA), while Schauble8 cyclised the same homoallylic alcohol 8 with bis(5>>m-collidine)iodine(I)perchlorate (Scheme 1.11). ...
... using a mixture o f sodium iodide and m-chloroperbenzoic acid (mCPBA), while Schauble8 cyclised the same homoallylic alcohol 8 with bis(5>>m-collidine)iodine(I)perchlorate (Scheme 1.11). ...
19.7 Reversible Addition Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones
... • However, the electronegative O increases this ...
... • However, the electronegative O increases this ...
Part I Carbohydrate Auxiliaries - Wiley-VCH
... The application of pseudo-enantiomers is of great importance when carbohydratederived chiral tools are used: While d-monosaccharides are easily available from the chiral pool, the corresponding l-enantiomers are mostly expensive and in some cases even unavailable. For the preparation of a pseudo-ena ...
... The application of pseudo-enantiomers is of great importance when carbohydratederived chiral tools are used: While d-monosaccharides are easily available from the chiral pool, the corresponding l-enantiomers are mostly expensive and in some cases even unavailable. For the preparation of a pseudo-ena ...
Modern Synthetic Methods for Copper-Mediated C(aryl
... condensation. At this point, there was little deliberation on the mechanistic rationale for these precise reaction conditions, although the outcome is of considerable importance. Chan and co-workers[18] first described a collection of Nand O-arylation transformations under novel reaction conditions ...
... condensation. At this point, there was little deliberation on the mechanistic rationale for these precise reaction conditions, although the outcome is of considerable importance. Chan and co-workers[18] first described a collection of Nand O-arylation transformations under novel reaction conditions ...
Elimination Reactions
... neutral conditions with polar solvents, such as water, ethyl alcohol or acetic acid. • E1 reactions can also occur with strong bases, but only at low concentration, about 0.01 to 0.1 M or below. • E2 reactions require strong base in high concentration, about 1 M or above. WWU -- Chemistry ...
... neutral conditions with polar solvents, such as water, ethyl alcohol or acetic acid. • E1 reactions can also occur with strong bases, but only at low concentration, about 0.01 to 0.1 M or below. • E2 reactions require strong base in high concentration, about 1 M or above. WWU -- Chemistry ...
Chapter - FIU Faculty Websites
... • Like gem-diol formation, the synthesis of acetals is reversible, and often, the equilibrium favors the reactants. • In acetal synthesis, since water is formed as a by-product, the equilibrium can be driven to the right by removing H2O as it is formed using distillation or other techniques. Please ...
... • Like gem-diol formation, the synthesis of acetals is reversible, and often, the equilibrium favors the reactants. • In acetal synthesis, since water is formed as a by-product, the equilibrium can be driven to the right by removing H2O as it is formed using distillation or other techniques. Please ...
Iodomethylzinc_iodid.. - Groupe Charette
... handled. Although the initial method of preparation of the Zn–Cu couple was difficult and not easily reproducible,7 several simpler and highly reproducible methods soon followed.11 Treatment of the Zn–Cu couple with CH2 I2 and a crystal of Iodine in Et2 O followed by heating to reflux generates the ...
... handled. Although the initial method of preparation of the Zn–Cu couple was difficult and not easily reproducible,7 several simpler and highly reproducible methods soon followed.11 Treatment of the Zn–Cu couple with CH2 I2 and a crystal of Iodine in Et2 O followed by heating to reflux generates the ...
1H-Imidazol-4(5H)-ones and thiazol-4(5H)
... hand, acid hydrolysis of these adducts efficiently affords N-alkylamino acid derivatives, as for instance the N-methylamino amide 21. Additionally, from the common adduct 26, functionalized polycyclic hydantoins of type 27 and 28 can also be synthesized. The authors proposed an heuristic model (Figu ...
... hand, acid hydrolysis of these adducts efficiently affords N-alkylamino acid derivatives, as for instance the N-methylamino amide 21. Additionally, from the common adduct 26, functionalized polycyclic hydantoins of type 27 and 28 can also be synthesized. The authors proposed an heuristic model (Figu ...
Copper-Catalyzed Coupling Reactions Using Carbon
... Oxidative coupling reactions with C-H bonds are quite challenging due to the relative strong C-H bond, along with the associated selectivity issues with the myriad of C-H bonds that are available for the coupling reaction. ...
... Oxidative coupling reactions with C-H bonds are quite challenging due to the relative strong C-H bond, along with the associated selectivity issues with the myriad of C-H bonds that are available for the coupling reaction. ...
aa-2005-38-71-negishi - University of Windsor
... cross-coupling tandem reaction were also reported in 1978.23 The use of Zn salts, such as ZnCl2 or ZnBr2, as additives or cocatalysts in the coupling step of this tandem reaction was shown to be highly desirable or even essential to observing satisfactory results. This study demonstrated, for the fi ...
... cross-coupling tandem reaction were also reported in 1978.23 The use of Zn salts, such as ZnCl2 or ZnBr2, as additives or cocatalysts in the coupling step of this tandem reaction was shown to be highly desirable or even essential to observing satisfactory results. This study demonstrated, for the fi ...
Transition Metal Reagents and Catalysts
... ®rst by giving a simple mechanistic explanation in chapter 2. Then a number of important types of reactions classi®ed mainly by representative substrates such as organic halides and allylic derivatives are surveyed with pertinent examples. For this purpose, I cited many references; these were select ...
... ®rst by giving a simple mechanistic explanation in chapter 2. Then a number of important types of reactions classi®ed mainly by representative substrates such as organic halides and allylic derivatives are surveyed with pertinent examples. For this purpose, I cited many references; these were select ...
Slide 1
... The pyridine ring is deactivated towards electrophilic aromatic substitution because of the electronegative nitrogen in the ring. Additionally the non-bonding electron on the nitrogen would react with the electrophile. Reaction only occurs under extreme conditions. Note: That substitution is in the ...
... The pyridine ring is deactivated towards electrophilic aromatic substitution because of the electronegative nitrogen in the ring. Additionally the non-bonding electron on the nitrogen would react with the electrophile. Reaction only occurs under extreme conditions. Note: That substitution is in the ...
dr.ebtehal Lec3
... Oxidation is the beginning of the deterioration process. Think of how a slice of apple turns brown when exposed to air. Oxidation leads to the formation of free radicals which are unstable molecules in the body that have one unpaired electron. They can cause oxidation and damage to the cells. This ...
... Oxidation is the beginning of the deterioration process. Think of how a slice of apple turns brown when exposed to air. Oxidation leads to the formation of free radicals which are unstable molecules in the body that have one unpaired electron. They can cause oxidation and damage to the cells. This ...
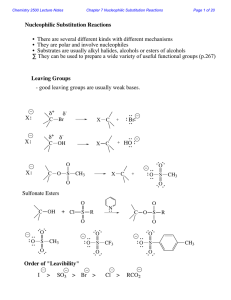
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
... Two mechanisms apply to most substitution reactions: SN1 and SN2 SN1: Substitution, nucleophilic, unimolecular SN2: Substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecular Which mechanism applies depends on the structure of your substrate. ...
... Two mechanisms apply to most substitution reactions: SN1 and SN2 SN1: Substitution, nucleophilic, unimolecular SN2: Substitution, nucleophilic, bimolecular Which mechanism applies depends on the structure of your substrate. ...
Elimination Reactions
... • E1 reactions occur under essentially neutral conditions with polar solvents, such as water, ethyl alcohol or acetic acid. • E1 reactions can also occur with strong bases, but only at low concentration, about 0.01 to 0.1 M or below. • E2 reactions require strong base in high concentration, about 1 ...
... • E1 reactions occur under essentially neutral conditions with polar solvents, such as water, ethyl alcohol or acetic acid. • E1 reactions can also occur with strong bases, but only at low concentration, about 0.01 to 0.1 M or below. • E2 reactions require strong base in high concentration, about 1 ...
A review of new developments in the Friedel–Crafts - Beilstein
... was discussed in the previous chapter. Even though it renders a convenient and environmental benign approach to 1,1diarylalkanes, there is still one stoichiometric side product formed during this transformation, namely water. Waste water treatment is an ongoing and expensive issue in large scale che ...
... was discussed in the previous chapter. Even though it renders a convenient and environmental benign approach to 1,1diarylalkanes, there is still one stoichiometric side product formed during this transformation, namely water. Waste water treatment is an ongoing and expensive issue in large scale che ...
Diels–Alder reaction
.png?width=300)
The Diels–Alder reaction is an organic chemical reaction (specifically, a [4+2] cycloaddition) between a conjugated diene and a substituted alkene, commonly termed the dienophile, to form a substituted cyclohexene system. It was first described by Otto Paul Hermann Diels and Kurt Alder in 1928, for which work they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1950. The Diels–Alder reaction is particularly useful in synthetic organic chemistry as a reliable method for forming 6-membered systems with good control over regio- and stereochemical properties. The underlying concept has also been applied to other π-systems, such as carbonyls and imines, to furnish the corresponding heterocycles, known as the hetero-Diels–Alder reaction. Diels–Alder reactions can be reversible under certain conditions; the reverse reaction is known as the retro-Diels–Alder reaction.