* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resources: http://sciencevideos
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
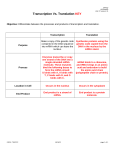
Essential Biology 7.3 & 7.4: Transcription and Translation (AHL) Resources: : Clegg pp 69-74 & 243-253, RG pp 38-41&122-128 You must also complete the Core (3.5) Essential Biology for this topic. 1. Distinguish between sense and antisense strands in DNA. The ______________ strand is complementary to the ___________ strand. The antisense strand is also known as the ____________ strand, as it is used for _____________ , to make mRNA. mRNA corresponds with the _____________ strand, with the exception of the base ___, which is replaced with ____. mRNA is complementary to the ________________ strand. 2. Describe the role of the antisense strand in transcription. 3. State the direction of transcription and draw a simple diagram to show the addition of an RNA molecule to a growing mRNA strand. http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 7.3 & 7.4: Transcription and Translation (AHL) 4. Outline the roles of the following regions of DNA in transcription: 5. Explain the process of transcription in prokaryotes, including the following: promoter region, RNA polymerase, 5’-3’ direction, free nucleoside triphosphates, complementary base pairing, terminator region. 6. Distinguish between introns and exons in eukaryotic DNA (DNA structure revision). 7. State one method of post-transcription modification of mRNA in eukaryotes. http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 7.3 & 7.4: Transcription and Translation (AHL) 8. Label the following regions on this tRNA molecule, stating the function of each: Acceptor stem, anticodon loop, hydrogen bonds. 9. tRNA needs to be activated in order to pick up the corresponding amino acid. Explain how tRNA is activated, including the role of a specific tRNA activating enzyme, ATP and amino acids. 10. Using a diagram, outline the structure of a ribosome, including protein and RNA composition, large and small subunits, three tRNA binding sites and mRNA binding sites. http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 7.3 & 7.4: Transcription and Translation (AHL) 11. Describe polysomes and state their function. 12. State the direction of movement of the ribosome along the mRNA strand (the direction of translation). 13. Explain the process of translation in four stages: Keywords: mRNA, ribosome, small subunit, large subunit, start codon, AUG, tRNA Explanation: 1. Initiation Keywords: amino acids, peptide bond, transfer, anticodon, tRNA Explanation: 2. Elongation Keywords: tRNA, mRNA, codon, release Explanation: 3. Translocation 4. Termination Keywords: stop codon, release/ detachment http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 7.3 & 7.4: Transcription and Translation (AHL) Explanation: 14. Draw and label the structure of a dipeptide. 15. Distinguish between polypeptides produced by free ribsomes and those produced by bound ribosomes, such as in the RER. (Revision: exocytosis) 16. Data based question (from IB Questionbank): It had always been assumed that eukaryotic genes were similar in organization to prokaryotic genes. However, modern techniques of molecular analysis indicated that there are additional DNA sequences that lie within the coding region of genes. Exons are the DNA sequences that code for proteins while introns are the intervening sequences that have to be removed. The graph shows the number of exons found in genes for three different groups of eukaryotes. [Source: Benjamin Lewin, (1999) Genes VII, OUP, page 55] http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 7.3 & 7.4: Transcription and Translation (AHL) Percentage of genes 100 80 Saccharomyces cerevisiae (a yeast) 60 40 20 0 40 30 Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly) 20 10 0 20 15 Mammals 10 5 0 1 a) 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 <30<40<60>60 Number of exons Calculate the percentage of genes that have five or less exons in mammals. ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Describe the distribution of the number of exons and the percentage of genes in D. melanogaster. ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... (2) (c) (i) Compare the distributions of the number of exons found in genes of S. cerevisiae and mammals. ............................................................................................................................... http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 7.3 & 7.4: Transcription and Translation (AHL) ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Suggest one reason for the differences in the numbers of exons found in genes of S. cerevisiae and mammals. ............................................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................................... (1) Human DNA has been analysed and details of certain genes are shown in the table below. Gene Insulin Gene size / kb* mRNA size / kb Number of introns 1.7 0.4 2 Collagen 38.0 5.0 50 Albumin 25.0 2.1 14 Phenylalanine hydroxylase 90.0 2.4 12 2 000.0 17.0 50 Dystrophin *kilobase pairs [Source: William S Klug and Michael R Cummings, (2002), Concepts of Genetics, 7th edition, Prentice Hall, page 314] (d) Calculate the average size of the introns for the albumin gene. ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 7.3 & 7.4: Transcription and Translation (AHL) ......................................................................................................................................... (2) (e) Analyse the relationship between gene size and the number of introns. ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... (2) (f) Determine the maximum number of amino acids that could be produced by translating the phenylalanine hydroxylase mRNA. ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... (1) Hemoglobin is a protein composed of two pairs of globin molecules. During the process of development from conception to adulthood, human hemoglobin changes in composition. Adult hemoglobin consists of two alpha- and two beta-globin molecules. Two globin genes occur on chromosome 16: alpha- and zeta-globin. Four other globin genes are found on chromosome 11: beta, delta, epsilon and gamma. The graph below illustrates the changes in expression of the globin genes over time. 50 Key: alpha-globin gamma-globin beta-globin delta-globin epsilon-globin zeta-globin 40 Percentage of hemoglobin 30 20 10 0 10 20 30 weeks of gestation 40 birth 2 6 4 month of age [Source: adapted from M Cummings, Human Heredity, 4th edition, West/Wadsworth Publishing Company] (g) State which globin genes are the first to be expressed after fertilization. http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com Essential Biology 7.3 & 7.4: Transcription and Translation (AHL) ......................................................................................................................................... (1) (h) Compare the expression of the gamma-globin gene with the beta-globin gene. ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... ......................................................................................................................................... (3) (i) Deduce the composition of the hemoglobin molecules - at 10 weeks of gestation: ............................................................................. - 2 months after birth: ............................................................................. (2) (Total 17 marks) http://sciencevideos.wordpress.com