* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Control miniQUIZ
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
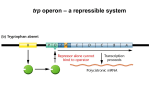
Cellular Control 1. Define the term ‘gene’. (1) 2. Proteins are long chains of amino acids joined by peptide bonds and can be either globular or fibrous. Name an example of each type. (2) 3. a) Define the term ‘genetic code’. b) Why must the genetic code be a three-letter code? (1) (1) 4. Identify the base that is found in RNA but not in DNA. (1) 5. During transcription a strand of DNA is used to synthesise a complementary mRNA sequence. Below is the sequence of DNA. Copy and complete the corresponding mRNA sequence. (1) -A C T G C G G T T A C G T A G-_____________________________6. The diagram below represents a polynucleotide that plays an important role in translation. Label the parts A–D. D A C B (2) 7. The diagram below illustrates protein synthesis. Label five important stages in this process. (5) B A C D E 8. State how glycogen phosphorylase is activated by cAMP. (1) 9. What is a mutation? (1) 10. Name a genetic disease caused by a single base mutation. (1) 11. Beneficial mutations are rare, but are very important to increase variation. Give one example of beneficial mutation. (1) 12. How does the lac repressor protein prevent transcription of the lac operon in the absence of lactose? (1) 13. On the diagram of the lac operon below, label components A and B. (1) Lac operon Regulator A B -galactosidase gene 14. Outline the main function of homeobox genes. (1) 15. Homeobox genes code for transcription factors. What do these do? (1) 16. The fruit fly (Drosophila melanogaster) is a key study organism in genetics. (2) T1 T2 T3 Using the diagram above answer the following questions: a) Which segment of the fruit fly develops wings? b) Are plant homeobox genes homologous to the homeobox genes in the fruit fly? 17. Apoptosis is important during development. Define the meaning of apoptosis and give an example. (1) Total /25