* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download With the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Human–animal hybrid wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
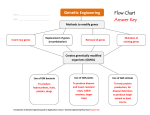
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
LTE 199H1S, L0422 - Genes, Genomes and Us Not offered in 2015-16 Lecturers: Prof. A. Bruce [email protected] Since the completion of the human genome sequence, we now have access to more information than ever before about our genetic make-up. The human genome contains 3 billion base pairs of DNA, encoding an estimated 25,000 genes, which are the basic units of heredity. This course addresses questions such as what are genes, how are they identified and how does knowledge about genes impact society at large. Students will explore the basic concepts that explain the genetic foundations of complex traits, with a major focus on how this information is used to understand, treat and potentially prevent human diseases. Topics include gene therapy, personalized medicine, cloning and stem cells. The significance of genomic research for understanding human biology, and the social consequences that may result from it, are discussed and debated. Evaluation is based on class discussions, oral presentations and written assignments.