* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Definition of the limbic system
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Blanchard's transsexualism typology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Emotion perception wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Orbitofrontal cortex wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
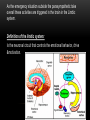
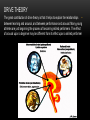
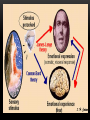
AROUSAL Prof. Dr. Elham Al-Jammas May 2015 L11 AROUSAL Is a state of being excited or alarmed or the establishment & maintenance of an awake state which involve a complex mechanism (mental& physical) ,that prepare the organism to deal with emergency situation & danger. The electrophysiological studies showed that both the thalamus & the cortex fire rhythmical burst of neuronal activities at a rate of 20-40c/s .During sleep the bursts are slow & not synchronized ,the higher the synchronization the higher the level of wakefulness. Stupor or coma indicates absence of arousal. Intense emotion usually involves physiological arousal caused by the activation of the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system that manifest by: -Rapid heartbeat & increased blood pressure. -Rapid breathing . -pupil dilate -Dryness of mouth & throat -feeling weak & even faint with sinking feeling in the stomach. -excessive sweating - trembling -poor concentration -blood sugar level increases As the emergency situation subside the parasympathetic take overall these activities are triggered in the brain in the Limbic system. Definition of the limbic system: Is the neuronal circuit that controls the emotional behavior, drive &motivation. The limbic system :is a set of brain structures including the hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, septum, limbic cortex and fornix, which seemingly support a variety of functions including emotion, behavior, long term memory, and olfaction The limbic system is the set of brain structures that forms the inner border of the cortex HIPPOCAMPUS AND ASSOCIATED STRUCTURES: Required for the formation of long-term memories and implicated in maintenance of cognitive maps. Amygdala: Involved in signaling the cortex of motivationally significant stimuli such as those related to reward and fear in addition to social functions such as mating. Fornix carries: signals from the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies and septal nuclei. Mammillary body: Important for the formation of memory; Cingulate gyrus: Autonomic functions regulating heart rate, blood pressure and cognitive and attentional processing Dentate gyrus: thought to contribute to new memories and to regulate happiness. Piriform cortex: The function of which relates to the olfactory system. Nucleus accumbens: Involved in reward, pleasure, and addiction Orbitofrontal cortex: Required for decision making. FUNCTION OF LIMBIC SYSTEM Limbic System: The Center of Emotions The limbic system operates by influencing the endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system. It is highly interconnected with the nucleus accumbens, the brain's pleasure center, which plays a role in sexual arousal and the "high" derived from certain recreational drugs. These responses are heavily modulated by dopaminergic projections from the limbic system. The limbic system is also tightly connected to the prefrontal cortex. Some scientists contend that this connection is related to the pleasure obtained from solving problems. To cure severe emotional disorders, this connection was sometimes surgically severed, a procedure of psychosurgery, called a prefrontal lobotomy (this is actually a misnomer). Patients who underwent this procedure often became passive and lacked all motivation Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: .The limbic system and the autonomic nervous system One of its most important effects is causing the adrenal glands (which sit on top of the kidneys) to release epinephrine (aka adrenalin) into the blood stream. Epinephrine is a powerful hormone that causes various parts of the body to respond in much the same way as the sympathetic nervous system. Being in the blood stream, it takes a bit longer to stop its effects. This is why, when you get upset, it sometimes takes a while before you can !calm yourself down again The sympathetic nervous system also takes in information, mostly concerning pain from internal organs. Because the nerves that carry information about organ pain often travel along the same paths that carry information about pain from more surface areas of the body, the information sometimes get confused. This is called referred pain, and the best known example is the pain some people feel in the left shoulder and arm when they are having a heart attack. The other part of the autonomic nervous system is called the parasympathetic nervous system. It has its roots in the brainstem and in the spinal cord of the lower back. Its function is to bring the body back from the emergency status that the sympathetic nervous system puts it into some of the details of parasympathetic arousal include... pupil constriction activation of the salivary glands stimulating the secretions of the stomach stimulating the activity of the intestines stimulating secretions in the lungs constricting the bronchial tubes decreasing heart rate The parasympathetic nervous system also has some sensory abilities: It receives information about blood pressure, levels of carbon dioxide in the blood, and so on. THE INVERTED-U THEORY The inverted U theory has been around for as long as the arousal/performance relationship has been studied. It simply states that the relationship between performance and arousal is curvilinear as opposed to linear, and takes the form of an inverted-U. it seems relatively clear that the nature of the relationship between athletic performance and arousal takes the form of the inverted U, it is not clear why this occurs. DRIVE THEORY The great contribution of drive theory is that it helps to explain the relationships • between learning and arousal, and between performance and arousal. Many young athletes are just beginning the process of becoming skilled performers. The effect of arousal upon a beginner may be different from its effect upon a skilled performer Thank You