* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download slides
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
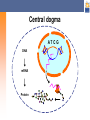
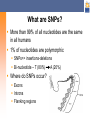
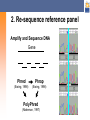
Selecting TagSNPs in Candidate Genes for Genetic Association Studies Shehnaz K. Hussain, PhD, ScM Assistant Professor Department of Epidemiology, UCLA [email protected] Epidemiology 244: Cancer Epidemiology Methods Objectives Molecular genetics primer Databases and tools to conduct in silico analyses for tagSNP selection/prioritization Central dogma ATCG DNA mRNA Protein What are SNPs? More than 99% of all nucleotides are the same in all humans 1% of nucleotides are polymorphic SNPs>> insertions-deletions Bi-nucleotide – T (80%) Where do SNPs occur? Exons Introns Flanking regions A (20%) What are haplotypes? A haplotype is the pattern of nucleotides on a single chromosome Two “copies” of each chromosome The haplotype inference problem ? T T ? C G G T? A A TA TT CG GG TA AA ? A T ? G G ? A A What is linkage disequilibrium? Linkage disequilibrium (LD) describes the nonrandom association of nucleotides on the same chromosome in a population One nucleotide at one position (locus) predicts the occurrence of another nucleotide at another locus No LD LD What are markers? Disease Phenotype Test for association between phenotype and marker loci Test for genetic association between the phenotype and the DSL LD Candidate gene Marker loci (SNPs) Disease Susceptibility Locus What are tagSNPs? TagSNPs are a subset of all SNPs in a gene that mark groups of SNPs in LD Avoids redundant genotyping LD Marker loci (SNPs) LD Disease Susceptibility Locus The joint effect of tagSNPs in cytokine genes and cigarette smoking in cervical cancer risk T-cell proliferation IL-2 IL-2 gene IFNγ gene IL-2 receptor Proliferation Proliferation of ofTH1-cells TH1-cells IFNγ Activated T-cell Background Cigarette smoking ↑ 1.5- to 3-fold cancer risk Cigarette smoking ↓ levels of IL-2 and IFNγ (cervical and circulating) ↓ levels of IL-2 and IFNγ HPV persistence in the cervix Cervical neoplasia Decreased survival from invasive cervical cancer Model Cigarette smoking SNPs in IL-2, IL-2R, and IFNG HPV-associated squamous cell cervical cancer Methods Study design Population-based case-only study Subjects 308 Caucasian squamous cell cervical cancer cases diagnosed 1986-2004 Residing in 3 western Washington counties Data collection Structured in–person interviews DNA isolated from buffy coats Multi-stage tagSNP design Select reference panel Re-sequence panel, identify SNPs (many markers, few subjects) Choose tagSNPs Genotype tagSNPs in main study (few markers, many subjects) 1. Select reference panel A sample of your study population Most representative Samples from the Coriell Repository Ability to integrate your data with other resources = Candidate gene SNPs = HapMap SNPs 2. Re-sequence reference panel Amplify and Sequence DNA Gene Phred Phrap (Ewing, 1998) (Ewing, 1998) PolyPhred (Nickerson, 1997) Alternatives to re-sequencing Program for Genomic Applications (PGA) SeattleSNPs – inflammation NIEHS SNPs – environmental response Innate Immunity International HapMap Project 5 million SNPs in four ethnically distinct populations 3. Choose tagSNPs Option LDSelect Tagger (Carlson, 2002) (de Bakker, 2005) r2 threshold Yes Yes SNP exclusions/inclusions No Yes SNP design score No Yes LDSelect output for IL-2 SeattleSNPs, r2≥0.80, MAF ≥0.05, Caucasian Bin Total Number of Sites 1 2 2 2 TagSNPs rs2069763 rs2069772 rs2069776 rs2069778 3 2 rs2069777 rs2069779 4 1 rs2069762 Genomic context Exons (cSNPs) SIFT (Ng, 2002) PolyPhen (Ramensky, 2002) Upstream flanking region Intron-exon junctions Sequence conservation UCSC Genome Browser, PhasCons (Siepel, Score 2005) Repeat region Unique region TagSNP summary Efficient yet comprehensive coverage of the genetic variation in our candidate genes Reduce costs Preference should be given to putatively functional variants: Literature, gene context, sequence conservation Thanks for your attention! Questions?