* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lecture 12 - McLoon Lab - University of Minnesota
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
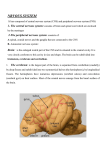
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Goal Today • Know the regions of the brainstem. • Know major landmarks of each region and be able to identify each region in cross section. • Understand the continuity of axon tracts from region to region. 2 Brainstem Geography • • Brainstem includes the medulla, pons and midbrain. All regions are visible on the ventral side of the brain. 3 Brainstem Geography • Not much of the brainstem is visible in a posterior view of the brain unless the forebrain and cerebellum are removed. 4 Brainstem Geography • The cerebellum covers the IV ventricle on the dorsal surface of the brainstem. 5 Brainstem Geography • The IV ventricle spans the entire pons and upper half of the medulla. 6 Brainstem Geography • The presence of the ventricle is used to distinguish upper and lower medulla. 7 Spinal Cord Review Tracts of ascending axons carrying sensory information: • Spinocerebellar tracts carrying proprioception • Dorsal columns carrying proprioception and deep touch (uncrossed) • Spinothalamic tract carrying pain, temperature and light touch (crossed) 8 Lower Medulla • Dorsal columns and dorsal column nuclei dorsal ventral ventral dorsal 9 Somatosensory Pathway: Dorsal Columns for Proprioception and Touch • The dorsal column axons synapse in nucleus gracilis and cuneatus. • The axons of these neurons cross the midline and form the medial lemniscus to thalamus. 10 Lower Medulla • Axons in the spinothalamic and spinocerebellar tracts continue up through the medulla. dorsal ventral 11 Lower Medulla • Pyramids are axons carrying motor information descending from cortex. 12 Lower Medulla • 90% of the axons in the pyramids cross in lower medullar forming the lateral corticospinal tract. • 10% remain as the anterior corticospinal tract. 13 Spinal Cord Review Tracts of descending axons carrying motor information from cortex: • Lateral corticospinal tract (crossed) • Anterior corticospinal tract (uncrossed) 14 Lower Medulla • Cranial nerves III – XII are attached to the brainstem . • All have nuclei (sensory and/or motor) in the brainstem. dorsal ventral ventral dorsal 15 Upper Medulla • IV ventricle (covered by cerebellum) • choroid plexus • openings into the subarchnoid space dorsal ventral ventral dorsal 16 Upper Medulla • Pyramids dorsal ventral ventral dorsal 17 Upper Medulla • Olive (external) and inferior olivary nucleus (internal) dorsal ventral ventral dorsal 18 Pons • Basal pons with pontine nuclei dorsal ventral ventral dorsal 19 Pons • Superior, middle and inferior cerebellar peduncles dorsal ventral ventral dorsal 20 Pons • Superior, middle and inferior cerebellar peduncles Ventral surface of the cerebellum 21 Pons • Corticopontine axons synapse in pontine nuclei • Neurons in pontine nuclei send their axons to the cerebellum via the middle cerebellar peduncle 22 Spinocerebellar Pathway • Spinocerebellar tracts enter cerebellum via superior and inferior cerebellar peduncles. 23 Pons • Corticospinal, corticopontine and corticobulbar tracts (motor) pass through pontine nuclei. 24 Midbrain • Cerebral peduncles (corticospinal, corticopontine, corticobubar tracts - motor) 25 Midbrain (lower) • Inferior colliculus (auditory) dorsal ventral ventral dorsal 26 Midbrain (lower) • Decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles dorsal 27 ventral Midbrain (upper) • Superior colliculus (vision) dorsal ventral ventral dorsal 28 Midbrain (upper) • Red nucleus – related to the cerebellum and the motor system dorsal 29 ventral Midbrain (upper) • Substantia nigra – sends axons to the basal ganglia; neurotranmitter is dopamine; degenerates in Parkinson’s disease dorsal 30 ventral Somatosensory Projection to Cortex Spinothalamic projection: • Primary sensory axons for pain, temperature and light touch synapse on neurons in the dorsal horn. • Axons of these dorsal horn neurons cross the spinal cord and ascend in the spinothalamic tract. • They synapse in the ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL) of the thalamus. • Axons from the VPL neurons project to somatosensory cortex. 31 Somatosensory Projection to Cortex Dorsal column projection: • Primary sensory axons for proprioception and touch enter the dorsal horn and ascend in the dorsal columns. • These axons synapse in nucleus gracilis (from lower body) and nucleus cuneatus (from upper body) in the medulla. • Axons from these nuclei cross the medulla and ascend to thalamus. • They synapse in the ventral posterolateral nucleus (VPL) of the thalamus. • Axons from the VPL neurons project to somatosensory cortex. 32 Somatosensory Pathway: Dorsal Columns for Proprioception and Touch • Medial lemniscus ascends through the brainstem to thalamus. 33 Somatosensory Pathway: Spinothalamic Tract for Pain, Temperature & Touch • Spinothalamic tract ascends through the brainstem to thalamus. 34 Somatosensory Pathway • Medial lemniscus (red) and spinothalamic (yellow) 35 Motor System • Axons of upper motor neurons descend from cortex. 36