* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Transport Power Point
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
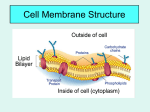
Cell Membrane • The cell membrane consists of a double layer of phospholipids. Layer 1 Attracts Water Layer 2 Repels Water Cell Membrane • The cell membrane controls/ regulates what enters and leaves the cell. • This allows the cell to maintain homeostasis. • Homeostasis is the process of maintaing a constant/stable internal environment. Cell Membrane • The cell membrane is selectively permeable. It “selects” which substances to allow in and out of a cell. • The cell membrane is permeable to substances that are able to cross the membrane. • Impermeable means substances are unable to cross the cell membrane. Impermeable Permeable Cell Transport (Movement Through the Cell Membrane) • Every cell has liquid on the inside and liquid on the outside. Cell Transport • One of the most important functions of the cell membrane is to regulate the movement of molecules from one side of the membrane to the other. • The molecules move through a solution which is the cytoplasm of the cell. Yeah! What is cytoplasm? Cytoplasm is the material inside a cell that contains the cell organelles Cytoplasm is a solution ?????? What is a solution? A liquid mixture of two or more substances in which the molecules of the substance are EVENLY mixed What is a solute? Gets dissolved in a solution What is a solvent? Does the dissolving in the solution Find A Friend and Think Solutions Think of 4 different solutions. Identify the solute and solvent in your solutions. Write down and turn in! Types of Cellular Transport • Passive Transport cell doesn’t use energy 1. Diffusion 2. Facilitated Diffusion 3. Osmosis • Weeee!!! high low Active Transport cell does use energy 1. Endocytosis 2. Exocytosis This is gonna be hard work!! high low Diffusion Across Cell Membrane Passive Transport Diffusion • In a solution, molecules move constantly. • Molecules tend to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. • This process ( moving from high to low) is called diffusion. • Diffusion does not require energy. Passive Transport Facilitated Diffusion • Does not require energy • Facilitated Diffusion: movement of certain molecules across the cell membrane with the assistance of a protein channel. Protein Channel Passive Transport Osmosis • Osmosis: the diffusion of WATER across the cell membrane. • Water will move across the cell membrane until equilibrium is reached. • Three ways cells are effected by osmosis: 1. Hypotonic 2. Hypertonic 3. Isotonic Osmosis Hypotonic Solution • Hypotonic: more water on the outside of the cell than the inside. • Water will diffuse from high to low causing water to enter the cell • This will cause the cell to swell and burst. • Cytolysis: the bursting of a cell Normal Blood Cell Blood Cell in Hypotonic Solution Hypotonic Solution Video Blood Cells http://www.linkpublishing.com/videotransport.htm#Blood-_Hypotonic_Solution Notebook Break 1) What “word” do you ALWAYS associate (think of) with osmosis? Water 2) In a hypotonic solution does a cell shrink or swell? The cell will swell. 3) What causes the cell to shrink or swell? The solution of water is greater on the outside of the cell so water will enter the cell. 4) What is cytolysis? The bursting of a cell How can you remember that a hypotonic solution makes a cell get bigger? • • Hypo = Hippo A hippo drinks lots of water and can be very BIG. • Hypo/Hippo makes a cell get bigger! Osmosis Hypertonic Solution • Hypertonic: more water on the inside of the cell than the outside of the cell. • Water will diffuse from high to low causing water to leave the cell • This will cause the cell to shrink. • Plasmolysis: the shrinking of a cell. Normal Blood Cell Blood Cell in Hypertonic Solution Hypertonic Solution Video Red Blood Cells http://www.linkpublishing.com/videotransport.htm#Blood_-_Hypertonic_Solution How can you remember that a hypertonic solution makes a cell get smaller? • • Hyper = Hyper kid in class. The teacher “kicks” the hyper kid out and the class size gets SMALLER (one less student) • Hyper/Hyper kid makes a cell get smaller! Osmosis Isotonic Solution • Isotonic: same amount of water on both the outside and inside of a cell. • Water flows evenly across the cell membrane • Cell is its normal size Isotonic Solution Video Red Blood Cells http://www.linkpublishing.com/videotransport.htm#Blood__Isotonic_Solution How can you remember that a isotonic solution makes a cell stay in a state of equilibrium? • • Iso = “ I so HAPPY! The amount water both inside and outside the cell are the same. It’s equal on both sides! • This mean the cell is “happy!” How well do you know your solutions in a cell? Identify each illustration as hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic. 2. 1. 4. 3. 6. 5. Active Transport • Requires energy • Movement from an area of low to high concentration • Two types of Active Transport: Endocytosis Exocytosis Movement of material into the cell Movement of material out of the cell En = In the cell Ex = Exit the cell Endocytosis Single celled organism engulfing food Phagocytosis: a very large particle moving across the cell membrane Exocytosis Osmosis Activitiy Hypotonic Hypertonic Osmosis Create a Crossword Puzzle with terms from Cell Membrane Notes and Cell Transport Notes. Create a Multiple Choice Test for the Cell Membrane Notes and Cell Transport Notes. Create a Cell Membrane and Cell Transport lesson to present to the class. Include visuals and examples. Minimum of 20 Minimum of 20 and choices A-D. Be prepared to teach the class Monday Isotonic Create a Fill In the Blank Story about the Cell Membrane and how substances are transported across the cell membrane. Minimum of 20 and provide a word bank.