* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cellular Communication - Sonoma Valley High School
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
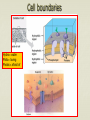
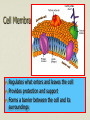
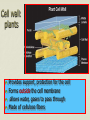
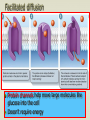
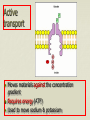
Cell boundaries Hydro= water Philic= loving Phobic= afraid of Cell Membrane Regulates what enters and leaves the cell Provides protection and support Forms a barrier between the cell and its surroundings 3 parts Lipid bilayer: a flexible sheet of 2 layers of lipid cells Protein channels allow large molecules to enter the cell Carbohydrate chains: act as identification cards Cell wall: plants Provides support, protection for the cell Forms outside the cell membrane allows water, gases to pass through Made of cellulose fibers Osmosis The diffusion of water If there is more water outside the cell, water will move in. If there is more water inside the cell, water will move out. Osmosis cont’d Hypotonic: cell has less water than the outside Hypertonic: cell has more water than outside Isotonic: concentrations are equal in and out Facilitated diffusion Protein channels help move large molecules like glucose into the cell Doesn’t require energy Active transport Moves materials against the concentration gradient Requires energy (ATP) Used to move sodium & potassium Endocytosis & Exocytosis Pockets or infoldings of the membrane can bring materials into or out of the cell Endo: materials are brought into the cell Exo: materials are released from cell via the Golgi apparatus Phagocytosis: “cell eating” macrophage ingesting e. coli bacteria