* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membrane
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
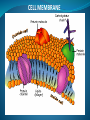
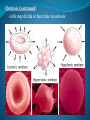
Cell Membrane - allows materials in or out of the cell Consists of: 1) Lipid Bilayer- 2 layers of fat tissue 2) Proteins- embedded into membrane - help move materials across Cell Membranes are: Selectively Permeable- controls what materials are allowed to cross. CELL MEMBRANE Cell Membrane Processes Diffusion - movement of materials from high to low concentration - diffusion requires no energy - continues until equilibrium is reached Osmosis - the diffusion of water * Water moves across when materials can’t Osmosis Continued: - cells may shrink or burst due to osmosis Facilitated Diffusion - use of proteins in the membrane that aid diffusion * Does not require energy!* Active Transport - using energy to move materials across the cell membrane. - used to fight natural diffusion Cell Transport Vocabulary Review A. Movement of water from high to low concentration B. The use of energy to move particles in/out of a cell C. Organelle that moves materials in/out of a cell D. Process of moving materials from high to low concentration E. Moving particles across a membrane without needing energy F. The use of proteins to move large particles in/out of a cell