* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life Science Notes – Diffusion/Osmosis/Active Transport
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
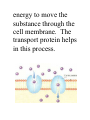
LS Chapter 3 section 2 Notes Diffusion/Osmosis/Active Transport The Cell Membrane is selectively permeable. Lets some substances pass in and out of the cell. Movement through the Membrane I. Functions: Protection Support Regulates what goes in and out of the cell (Takes in oxygen, food, and water/eliminates wastes.) Three Methods that move substances in and out of the cell are; 1. Diffusion 2. Osmosis 3. Active Transport Diffusion moves molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Concentration = the amount of substance in a given volume. (p.81) Molecules are always moving. They bump into each other and spread apart. Osmosis is diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. This is passive transport. NO ENERGY IS NEEDED Cells cannot function properly without adequate water. Active Transport is the movement of material through cell membrane using energy. If a substance of higher concentration is inside the cell and the cell needs to take in more of that substance it will need to use its energy to move the substance through the cell membrane. The transport protein helps in this process. Transport by Engulfing – The Amoeba uses active transport by surrounding, engulfing, and wrapping around a particle. It forms a vacuole. This cell uses energy in this process. (Phagocytosis & pinocytosis)