* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 6- Cell membrane and Cell transport study guide:
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
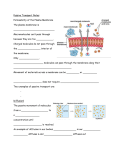
Chapter 6- Cell membrane and Cell transport study guide: 6.2 Key Terms: phospholipid bilayer Concepts and Objectives: Describe how large molecules move across a membrane Describe the structure of cellular membranes. Identify all the functions of proteins in cellular membranes. Describe how phospholipid molecules are oriented in the plasma membrane of a cell. What is the function of a transport protein? 6.3 Key Terms: diffusion equilibrium selectively permeable membrane passive transport facilitated diffusion osmosis hypertonic hypotonic isotonic active transport vesicle exocytosis endocytosis Concepts and Objectives: Relate diffusion and equilibrium. Describe how passive transport occurs. Relate osmosis to solute concentration. Explain how active transport differs from passive transport. Describe how large molecules move across a membrane. Distinguish between hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions, and give an example of how each affects an animal cell. Make a concept map of the different types of transport, which require energy, how molecules move, and which require transport proteins. Review of Transport Worksheet: What happened in the starch and iodine demos in class? Egg Osmosis Worksheet and Demo: What occurred in the different stages of the egg demo? Which solutions were hypotonic and hypertonic? How did water move across the egg membrane Plasmolysis Lab: Review what happened when salt was added to the plant cells. 15% salt was what type of solution compared to the normal plant cell environment? What happened to the central vacuole, and chloroplasts? What effect did the cell wall have on the plant cell?