* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Osmosis - Perry Local Schools
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
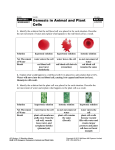
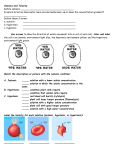
Friday, January 4 Bell Work: Complete day 3 of the Observing Osmosis Lab. The corn syrup solution goes into the bucket, not the sink. Osmosis: Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. Important because cells cannot function properly without enough water. 1 Isotonic (Equal) Hypotonic (Under) Hypertonic (Over) Isotonic • Water moves in and out of the cell at the same rate. • H2O concentration inside equals H2O concentration outside • Cells retain normal shape 2 Isotonic Hypotonic • Water moves into the cell causing it to swell. • Extremely hypotonic solution can cause plasma membrane to burst. • Plant cells do not burst because of cell wall. Plant appears plump. • Reason why grocery stores mist water on produce. 3 Hypotonic Hypertonic • Water flows out of the cell • Animal cells shrivel because of loss of water • Plant cells the cell membrane and cytoplasm shrink away from the cell wall • Causes wilting of plants. 4 Hypertonic 5