* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6.3 Reading Guide
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
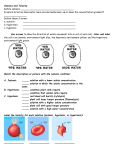
NAME DATE Website: biology.com 6.3 Membranes regulate the traffic of molecules Reading Guide 1) Define the following key terms: DiffusionEquilibriumVesicle2) The passive transport of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called 3) The solution with a higher concentration of solute is said to be hypertonic. What does “hyper” mean? 4) The solution with the lower solute concentration is said to be hypotonic What does “hypo” mean? 5) Solutions in which the concentrations of solute are equal are said to be isotonic What does “hyper” mean? 6) What role does a cellular membrane play in passive transport? 7) Distinguish between hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions, and give an example of how each affects an animal cell. Solution Hypertonic How can it affect an animal cell Hypotonic Isotonic 8) Explain the difference between exocytosis and endocytosis Exocytosis: Endocytosis: 9) What role does active transport play in cell function? 10) How do vesicles transport large molecules out of the cell?