* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psychology 101 Exam 1
Functionalism (philosophy of mind) wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Trans-species psychology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Mental chronometry wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Mental image wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural binding wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
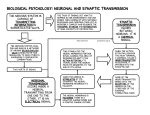
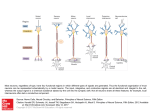
Name: ____________________ Date: ____________________ Psychology 101 Exam 1 Fall 2004 “On my honor, I have neither given nor received aid on this exam.” _________________________ Part I: Multiple Choice 1) Clinical neuropsychologists work specifically with tests designed to diagnose the effects of a. Childhood trauma b. Brain damage c. Psychological disorders d. Sleep deprivation 2) __________ help in the general care and feeding of neurons. a. Neural circuits b. Axons c. Glial cells (p. 47) d. Cell bodies 3) According to Stanovich and lecture, which of the following is the LEAST helpful approach in answering scientific questions a. Case studies b. Essentialism c. Operational definitions d. Systematic Empiricism 4) The idea of a chopstick gene refers to the idea that: a. There is likely a gene for eating behavior b. There is a gene (or genes) that produce differences between racial groups c. Differences between groups may result from an indirect effect of genetics d. Gene splicing can affect phenotypes 5) The naturalistic fallacy refers to the idea that: a. Nature is more important than nurture b. One cannot derive moral imperatives from what nature produces c. Nature is not logically prior to environment d. Genetic influences on behavior are usually overrated 6) According to the idea of culture of honor a. The South is more violent that the North because it was settled by herders b. White but not necessarily black males in the South should be more angered by insults c. The South should have elevated levels of argument related violence but not of felony related (i.e., violence committed during a robbery) d. All of the above 7) Which of the following is not, according to Pinker, a doctrine that guides our thinking about humans a. The blank slate b. The ghost in the machine c. The irrational theorist d. The noble savage 8) Which of the following likely results from failures of people to appreciate randomness a. The fallacy of the hot hand b. Essentialism c. Reliance on case studies d. Intuitionism as a source of perceived correctness or likelihood 9) Long term potentiation refers to a. The effects of genetic hard-wiring on neural transmission b. The growth of connections among specific neurons c. The decay of neural connections that are not used very often d. The potential of every neuron to both facilitate and inhibit neural firing 10) All of the following are true concerning genes EXCEPT: a. Genes play a role in preferences b. Genes are not affected by the environment c. Genes can copy themselves d. Genes make proteins 11) According to the Bernhardt article and lecture, all of the following brain structures have been implicated in violence EXCEPT: a. Frontal cortex b. Hypothalamus c. Thalamus d. Amygdala 12) According to lecture all of the following are examples of incorrect probabilistic reasoning EXCEPT: a. Using single cases to disprove a well established cause b. Stereotypic thinking c. Assigning salience to low probability events d. Reliance on base rates 13) A situation in which a science major does well in a physics course but not in a poetry course and an English major shows the reverse pattern is an example of: a. Cross over interaction b. Main effect c. Direction effect d. Main effect and interaction 14) In correlation and experimental studies, the designated cause is the a. Dependent variable b. Independent variable c. Third variable d. Main effect 15) Most of the brain’s mental processes occur in the __________. a. Ventricles b. Gyrus c. Cerebral cortex d. Meninges 16) The sympathetic division of the nervous system is to the parasympathetic division of the nervous system as a. Helpful is to hindrance b. Assist is to prevent c. Activate is to inhibit d. Inhibit is to activate 17) Our physical environment affects us at the level of a. Brain b. Group c. Brain and person d. Brain, group and person 18) The Structuralists were important in the history of psychology because they a. Examined consciousness and the structure of mental processes b. Realized the limits of introspection and focused on the structure of behaviors c. Were strongly influenced by Charles Darwin d. Began the cognitive revolution. 19) From a scientific perspective, a major problem with Psychodynamic theory is that it a. Focuses too much on sex b. It is difficult to test its principles c. Mental processes are hidden from awareness d. There is no unconscious 20) The part of the neuron that sends information is called the _________. a. Dendrite b. Axon c. Myelin sheath d. Terminal button 21) The two halves of the brain are connected by the __________. a. Cerebral hemisphere b. Sulcus c. Corpus callosum d. Gyrus 22) According to lecture, two sources of the causality problem in Correlational studies are a. Main effects and interactions b. Directional effects and third variables c. Third variables and main effects d. Direction effects and interactions 23) Which of the following have been linked with aggression? a. Increased levels of serotonin b. Decreased levels of testosterone c. Increased levels of testosterone and decreased levels of serotonin d. Decreased levels of testosterone and increased levels of serotonin 24) According to John Locke in Steven Pinker’s The Blank Slate, how do people acquire knowledge? a. Intuition b. Mental Processing c. Heredity d. Experience 25) DNA triads that specify proteins are called a. Axons b. Introns c. Exons d. Neurons 26) The paradox of environmental equality is that a. It is hard to equate environments b. We do not know how to measure environments c. To the extent environments are equal, heredity factors would be more important factors in individual differences d. Because genes affect environmental choices, environments can never be equal 27) The second messenger system in neural transmission refers to a. The fact that several neurotransmitters affect the same neuron b. The secondary affects inhibition of neural firing c. Messages sent to various neural control centers about rates of neural firing d. Chemicals that facilitate growth of additional neural receptors when the neuron fires 28) According to lecture, violent men are more likely to a. See violence as leading to rewards b. Abuse alcohol and drugs c. Have bi-polar disorder d. All of the above 29) According to Pinker, a major problem of Twentieth Century anthropology is that it a. Bases generalizations on study of too few cultures b. Relies too heavily on behaviorism and psychoanalysis c. Assumes that there is no basic human nature d. Does not rely heavily enough on modern psychology 30) With regard to mental processes, some behaviorists (such as Skinner) suggested that a. Mental processes play no role in behavior b. Mental processes were the most important aspects of behavior c. Behaviors could not be understood without also studying mental processes d. Mental processes were what made human behavior different from animal behavior 31) An important contribution of cognitive psychology was a. The development of computers b. Focusing on unobservable mental processes c. Making the analogy between computer software and mental processes d. Using the brain to study mental processes 32) Evolutionary psychology suggests that certain cognitive strategies and goals are built into the brain because a. They help humans adapt to their natural environment b. Human brains are similar to the brains of higher primates c. They are the result of learning that has taken place over many centuries d. All humans, even infants quickly learn that they are effective strategies 33) If a psychologist is studying test anxiety by examining the way that students’ thoughts prior to an exam affect their feelings about the exam, the psychologist is primarily looking at events at the level of the _______________. a. Brain b. Person c. Group 1. Environment 34) Reuptake refers to a. An area where neurotransmitters or neuromodulators attach themselves b. The process by which the surplus neurotransmitter is reabsorbed back into the sending neuron c. A chemical that mimics the effect of a neurotransmitter d. A chemical that blocks the effect of a neurotransmitter 35) Which of the following approaches is most likely to establish clear causality a. Case studies b. Correlational studies c. Surveys d. Experiments 36) In The Blank Slate, what concept is often attributed to Descartes that often accompanies the Blank Slate doctrine? a. Leviathan b. The Ghost and the Machine c. Dualism d. The Noble Savage 37) The SRY gene is responsible for a. determining sex b. producing neurotransmitters c. producing amino acids d. copying other genes 38) Monozygotic twins have ______ genetic overlap. a. 100% b. 75% c. 50% d. 25% 39) If an individual believed that why people feel and think the way they do is more important than what they think and how they think, this individual would most likely be a proponent of the _____________ approach to psychology. a. Structuralist b. Functionalist c. Psychodynamic d. Gestalt 40) The precise location where communication between neurons occurs is __________. a. Synaptic cleft b. Terminal button c. Myelin sheath d. Neurotransmitter Part II: Short Answer. Please choose and answer 3 of the 5 questions below. 1) What are operational definitions, and how do they relate to essentialism? 2) According to Stanovich what is the principle of connectivity? 3) What does it mean to say that nature does not necessarily parse psychological phenomena the way psychologists do? 4) According to Pinker, what are the differences between greedy and good reductionism? 5) What is the illusory correlation? Give at least two examples (extra points for an example not discuss in Stanovich).