* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 19 - Biology Junction
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
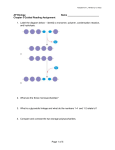
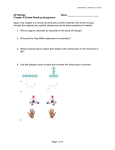
Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp AP Biology Chapter 19 Guided Reading Assignment Name _________________________ 1. Define the following terms: a. Chromatin b. Nucleosome 2. Outline the levels of DNA packing in the eukaryotic nucleus below next to the diagram provided. 3. What is the difference between heterochromatin and euchromatin? Which is transcribed? 4. What is cell differentiation? 5. IF cells carry all of the genetic differences, why then are cells so unique – what is responsible for this? Page 1 of 6 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp 6. In the diagram below – highlight all of the potential locations for gene expression regulation in eukaryotic cells. How does this compare with prokaryotic cells? 7. What effect do the following have on gene expression? a. Histone acetylation b. Histone deacteylation c. DNA methylation 8. How does methylation relate to genomic imprinting? Page 2 of 6 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp 9. Define epigenetic inheritance. 10. How do the following control elements assist in regulation? a. Transcription factors b. Enhancers c. Activators d. Repressors 11. Use the diagram below to explain the interactions of enhancers and transcription activators. 12. Explain how RNA processing is a mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation. 13. What role do microRNA’s play in post-transcriptional regulation? Use the diagram below to help you explain. Page 3 of 6 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp 14. What is RNA interference? 15. How does translation provide another opportunity for control? 16. What is a proteasomes? 17. What is the difference between oncogenes,proto-oncogenes and tumorsuppressor genes? 18. What is the ras gene? 19. What is the p53 gene? 20. Label the diagram below that describes the signaling pathways that regulate cell division. Page 4 of 6 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp 21. Why is said that people inherit predispositions to cancer not cancer itself? 22. What are the types of DNA sequences in the human genome and what % of the genome are they? 23. What is the difference between transposons and retrotransposons. Use the diagram below to help you answer the question. Page 5 of 6 Adapted from L. Miriello by S. Sharp 24. What are Alu elements? 25. What are multi-gene families? 26. What are pseudogenes? 27. How can errors during meiosis lead to duplication of genes? 28. What are three ways transposable elements are thought to have contributes to the evolution of the genome? . Page 6 of 6