* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download protein synthesis - Ms. Dooley`s Science Class
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Holliday junction wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
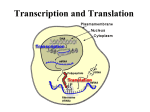
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS This activity will help you become more familiar with the process of protein synthesis and will help distinguish between transcription and translation. Use your book to help review any problems. PART 1 - Transcription During transcription, the DNA double helix “unzips”. As the hydrogen bonds between the two strands break, nucleotides floating in the nucleus line up next to the nucleotides of one DNA strand (“master strand”) to form mRNA. (Remember that uracil replaces thymine in the RNA formation; therefore, uracil pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine.) The nucleotides on the new mRNA are complimentary (opposite) to the nucleotides in the master strand of DNA. After the mRNA is formed, it passes out of the nucleus to go into the cytoplasm. 1. One strand of DNA has the base sequence: GCATTGGCAGTCATG. Write what the strand of mRNA would like: 2. A strand of genetic code reads: CCATTGGATAA. Is this a strand of DNA or RNA? How do you know? PART 2 – Translation (I) Once the mRNA has left the nucleus, it travels to a ribosome. There, the rRNA and ribosome together read the mRNA in groups of three (codon). Each codon codes for a specific amino acid (translation). the Genetic Code chart to decode the correct amino acid for the following codons: 3. UUA: 11. GGG: 4. GAG: 12. CCA: 5. UAU: 13. GCU: 6. CUA: 14. AGA: 7. AUC: 15. GGG: 8. UUG: 16. UGG: 9. AAA: 17. UGU: 10. UUU: PART 3 – Translation (II) Once the ribosome reads the codon, an anticodon (tRNA) becomes attached to the mRNA. The attachment of the tRNA to the mRNA continues until a termination (stop) codon is read. At this point, the tRNA detaches and the protein chain of amino acids is left. The tRNA goes back into the cytoplasm to pick up more amino acid. Determine the tRNA (anticodon) for each codon below: 18. GGU : 20. AUG : 19. CGC: 21. AAA: 22. CUG : Conclusions 23. Write the mRNA that would be transcribed from the following strand of DNA: GTA-TAC-CAG-TCA-TTT-GTC 24. Using your answer from #23 (above), write the amino acid sequence which would be translated: 25. If there was a mistake in transcribing the DNA strand from #23 and the mRNA read: CAA-AUG-GUC-AGU-AAA-CAG, how many mistakes were there made in transcription? 26. Using your answer to #25, what is the new amino acid sequence that would be translated? 27. What is a change in the genetic code called?