* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA to Protein Synthesis
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Histone acetylation and deacetylation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
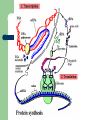
DNA Transcription & Protein Translation Honors Biology Today’s Objectives Investigate and understand common mechanisms of protein synthesis. DNA Transcription DNA must be copied to messenger RNA (mRNA) mRNA goes from nucleus to the ribosomes in cytoplasm mRNA complements known as codons – Only 3 nucleotide “letters” long Remember RNA has uracil (U) instead of thymine (T)! Transcription – Step I A C G T A T C G C G T A T G C A T A G C G C A T Template DNA Strands Transcription – Step II A C G T A T C G C G T A U G C A U A G C G C A U Template DNA is Matched Up with Complementary mRNA Sequences Transcription – Step III A C G U A U C G C G U A U G C A U A G C G C A U mRNA leaves nucleus and goes to ribosomes A new complementary RNA strand is made (rRNA) Transcription Reminders The template strand is the DNA strand being copied The rRNA strand is the same as the DNA strand except Us have replaced Ts Protein Translation Modified genetic code is “translated” into proteins Codon code is specific, but redundant! – – 20 amino acids 64 triplet (codon) combinations How to find the Amino Acid… tRNA in cytoplasm has a codon attached to an amino acid tRNA structure 3-base code (triplet) is an “anticodon” Protein molecule Attached amino acid that is carried from cytoplasm to ribosomes Protein Synthesis Start: Ribosome binds to mRNA at start codon (AUG) Elongation: – – – tRNA complexes bind to mRNA codon by forming complementary base pairs with the tRNA anticodon The ribosome moves from codon to codon along the mRNA. Amino acids are added one by one Release: release factor binds to the stop codon