* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1st 6 Test Review Notes 2012
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
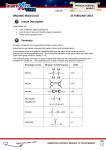
1st 6wks Review (This review will cover most of the six weeks test but not every question; use your spiral to study for the test.) Safety 1. Basic equipment a) Safety goggles b) Apron c) Gloves d) Additional equipment as directed by teacher 2. Safety Rules a) Follow all teacher directives b) Report accidents immediately c) Understand and follow all warning signs and labels d) Do not play in the lab e) Never eat or drink in the lab f) Wear closed toed shoes when directed g) Tie back long hair h) Do not taste drink or smell anything without teacher permission i) Clean up lab area before leaving Chemistry Atoms The smallest unit that still has the properties of an element Made up of protons, neutrons and electrons Molecule Is made up of two or more atoms The atoms in a molecule may be of the same element or different elements Compound Is made up of two or more different elements Chemical symbols 1st letter in all element symbols is capitalized 2nd letter in all element symbols is lower case Chemical Formula The coefficient (number in front of element/compound) in an element/compound represents the number of molecules in that element/compound The subscript (number below the last letter in an element) represents the number of atoms in that particular element. Models Models are manmade representations of real world situations Have limitations that prevent them from showing every aspect of what is being studied. Example: a model of the universe cannot be made to scale in a classroom and still be visible to the naked eye. Types of scientific investigations Descriptive investigation Uses observations to record interactions between an object and its environment/test conditions Records the observations as data Uses recorded observations to form a conclusion Comparative investigation Uses observations/tests results to compare and contrast 2 or more objects with each other Records observations/tests results as data Uses data to form a conclusion by comparing, contrasting, and showing relationships between two or more objects. Experimental investigation An investigation where a scientist tests their hypothesis by changing one variable and seeing the effect on a second variable. There is only 1 independent variable and it is the variable you control/change Dependent variable is the variable affected by the independent variable Constants everything that does not change at anytime during the experiment Control group establishes the base line for the experiment Cells Parts of a cell Cell membrane-provides structure to cell Cell wall-provides strength and shape to plant cells Nucleus-were genetic information is contained for cellular reproduction. Directs activities within the cell, sometimes referred to as the command center or the brain of the cell. Cytoplasm- is a flowing jelly like material that other cell organelles are contained in Mitochondrion- the cell organelle that produces energy used within the cell Chloroplast- plant cell organelle that contains chlorophyll and were plant cell photosynthesis occurs Vacuole- storage organelle for the cell. Stores items such as water and proteins. Large in plant cells, small but usually numerous in animal cells. Types of cells Prokaryotic cell-primitive cell form has no nucleus. Example is a bacteria cell Eukaryotic cell-modern cell form has a nucleus. Example animal cells Cell forms Animal cell Plant cell Cell theory 3 major components of cell theory All living organisms are composed of cells. The cell is the basic unit of life Cells arise from pre-existing cells. Scientists who contributed to cell theory Hans and Zacharias Janssen-1590 inventors of 1st compound microscope Robert Hooke-1665 used the word “cell” to describe microscopic structures Francesco Redi-1668 disproved the idea of spontaneous generation Anton Von Leeuwenhoek-1674 first to see and describe bacteria Robert Brown-1831 discovered the cell nucleus Matthias Scleiden-1839 proposed that all living things are made up of one or more cells. Theodor Schwann-1839 formulated the cell theory of life Rudolf Virchow-1855 every cell stems from another cell Organic compounds All organic compounds must contain Carbon and one of the following elements H-Hydrogen O-Oxygen N-Nitrogen P-Phosphorus S-Sulfur All living organisms are made up mostly of water and organic compounds Turgor pressure A force exerted outward on a plant cell wall by the water contained in the cell. This force gives the plant rigidity, and may help to keep it erect.