* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Chemistry Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
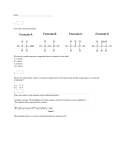
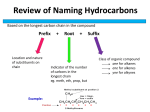
Organic Chemistry Review Alkanes: Hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds between carbon atoms; alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon-carbon double bond; alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkynes: a hydrocarbon that contains a carbon-carbon triple bond; alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbon: an organic compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen. Isomer: compounds that have the same molecular formula but different molecular structures. Unsaturated compound: an organic compound with one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. Saturated compound: an organic compound in which all carbon atoms are joined by single covalent bonds; it contains the maximum number of hydrogen atoms. Functional group: a specific arrangement of atoms in an organic compound that is capable of characteristic chemical reactions; the chemistry of an organic compound is determined by its functional group. Hydroxyl: the –OH functional group present in alcohols. I.U.P.A.C: The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations that represents chemists in individual countries. Substituent: an atom or group of atoms that can take the place of hydrogen atom on a parent hydrocarbon molecule. Alkyl group: a hydrocarbon substituent. Ester: a derivative of a carboxylic acid in which the –OH of the carboxyl group has been replace by the -OR from the alcohol. Carbonyl group: a functional group having a carbon atom and an oxygen atom joined by a double bond. Organic compound: compound containing carbon. Distillation: Crude oil is heated so that it vaporizes and rises through a fractionating column. Compounds with the highest boiling points condense near the bottom where it is hotter. Cracking: Controlled process by which hydrocarbons are broken down into smaller more useful molecules. Esterification: reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol to form an ester and water. Alcohol: an organic compound having an –OH (hydroxyl) group attached. Carboxylic acid: an organic acid containing a carboxyl group. Carboxyl group: a functional group consisting of a carbonyl group attached to a hydroxyl group. 2. a) CnH2n+2 b) CnH2n c) CnH2n-2 d) CnH2n e) R-OH f) R-COOH g) R-COO-R1