* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chemistry: Unit Organizer Name 6-__ Matter has physical properties
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear transmutation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical element wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
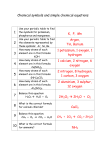
Chemistry: Unit Organizer Name ____________________________________________ 6-__ Matter has physical properties that can be used for classification. You can compare metals, nonmetals, and metalloids using physical properties such as luster, conductivity, or malleability. You can use the physical property calculate density to identify an unknown substance. Know the differences between elements and compounds. Know that an element is a pure substance represented by chemical symbols. You can recognize that a limited number of the many known elements comprise the largest portion of solid Earth, living matter, oceans, and the atmosphere. You can differentiate between elements and compounds on the most basic level. You can identify the formation of a new substance by using the evidence of a possible chemical change such as production of a gas, change in temperature, production of a precipitate, or color change. Physical property: property of matter that can be observed or measured without changing the matter (ex. length, mass, volume, shape, color, density, luster, malleability, ductility, conductivity). Prokaryotes Physical change: change in a physical property in which the identity of the matter does not change (ex. breaking a piece of glass into pieces.) Some, but not all physical changes can be reversible. You could refreeze the water into ice, but you cannot put your hair back together if you don’t like your haircut! Chemical property: Any characteristic that gives a substance the ability to undergo a change that results in a new substance. (Remember: there are only two kinds of chemical properties: ex. Eukaryotes ability to react with other substances or flammability). Chemical change: change in a chemical property in which the identity of the matter does change into a new substance (ex. digestion, respiration, photosynthesis, burning, and decomposition.) Change in a substances' state of matter are called phase changes. Element: a pure substance represented by a symbol on the periodic table of elements. cannot be separated into any other kinds of matter by any physical or chemical process. made up of identical atoms. make up matter on the earth For example: H & O are elements, but together H20 is a molecule. 3 Naming Rules for the Chemical Symbols of Elements: Rule 1: PRINT all symbols. Rule 2: If there is only one letter, that letter is always a capital. o Example: H for hydrogen Rule 3: If there are two letters, the first letter is a capital and the second is lower case. o Example: He for helium Know the Chemical Symbols of Common Elements: A limited number of the many known elements comprise the largest portion of solid Earth, living matter, oceans, and the atmosphere. Symbol 0 N C Na H Cl Fe Al Si Ca Element Oxygen Nitrogen Carbon Sodium Hydrogen Chlorine Iron Aluminum Silicon Calcium Compound: A substance made up of two or more different types of atoms (elements). to determine the number of elements in a compound: count the Capital letters. Compounds are substances made of two or more elements chemically combined in a set ratio. made of more than one kind of element. can be broken down during a chemical reaction. represented with elements symbols and subscripts (H20). Subscripts tell how many atoms of each element are in the compound. If there is no subscript, there is only 1 atom of that element. Example: glucose = C6H12O6 6 atoms of carbon, 12 atoms of hydrogen and 6 Evidence of a chemical change: Remember that compounds are two or more elements that combine chemically to create a new substance. The following can be used as evidence that a chemical reaction occurred: Temperature change Solid precipitate forms Color change Gas bubbles form atoms of oxygen Vocabulary: Ability to react: When a substance has the potential to react with acid, oxygen or water; a chemical property. Atom: The smallest unit of matter. ex. a carbon atom Chemical Reaction: a process in which chemical bonds are broken and atoms rearranged. During the process a new substance is formed. Compound: 2 or more elements combined to make something new, Ex. Na (sodium) + Cl (chlorine) = NaCl (salt) Density:The measurement of how much mass of a substance is contained in a given volume; compactness of matter. Element: A pure substance that cannot be broken down into smaller parts. Composed of identical atoms. Flammability: Ability of a substance to ignite, causing fire or combustion; chemical property. Oxidation/rust: A chemical reaction in which a substance, such as iron, combines with oxygen to form a new substance. Phase Change: A change in the state of matter. ex. going from a solid to a liquid; a physical property. Product: The substance(s) that are formed/released in a chemical reaction. State of Matter or Phase of matter: The state in which matter can exist: solid, liquid and gas; a physical property.