GPS semester review
... ____ 28. Elements are placed in the same column of the periodic table because their outer electrons are in the same energy level. ____ 29. The N2 molecule is nonpolar. ____ 30. Nonpolar molecules have a slight negative charge on one end and a slight positive charge on the other. ____ 31. According ...
... ____ 28. Elements are placed in the same column of the periodic table because their outer electrons are in the same energy level. ____ 29. The N2 molecule is nonpolar. ____ 30. Nonpolar molecules have a slight negative charge on one end and a slight positive charge on the other. ____ 31. According ...
chapter 4 types of chemical reactions and solution
... happens. Dalton’s atomic theory explains why mass is conserved in a chemical reaction. The kinetic molecular theory explains why pressure and volume are inversely related at constant temperature and moles of gas present, as well as explaining the other mathematical relationships summarized in PV = n ...
... happens. Dalton’s atomic theory explains why mass is conserved in a chemical reaction. The kinetic molecular theory explains why pressure and volume are inversely related at constant temperature and moles of gas present, as well as explaining the other mathematical relationships summarized in PV = n ...
Answers to SelectedTextbook Questions
... solid (graphite) or a hard crystalline material (diamond). Both are network solids. Hydrogen and oxygen are both colorless diatomic gases. (a) In CO, there is one carbon atom for every oxygen atom (or the ratio of C to O atoms is 1:1). (b) In CH4, the C to H atom ratio is 1:4. (c) In C2H2, ...
... solid (graphite) or a hard crystalline material (diamond). Both are network solids. Hydrogen and oxygen are both colorless diatomic gases. (a) In CO, there is one carbon atom for every oxygen atom (or the ratio of C to O atoms is 1:1). (b) In CH4, the C to H atom ratio is 1:4. (c) In C2H2, ...
Modern Analytical Chemistry
... An additional problem is encountered when the isolated solid is nonstoichiometric. For example, precipitating Mn2+ as Mn(OH)2, followed by heating to produce the oxide, frequently produces a solid with a stoichiometry of MnOx , where x varies between 1 and 2. In this case the nonstoichiometric produ ...
... An additional problem is encountered when the isolated solid is nonstoichiometric. For example, precipitating Mn2+ as Mn(OH)2, followed by heating to produce the oxide, frequently produces a solid with a stoichiometry of MnOx , where x varies between 1 and 2. In this case the nonstoichiometric produ ...
volume 2 - PianetaChimica
... atmospheric liquid water pool of 5000 m3 and fully returned on earth as rain, what is the expected pH of the condensed water? 3.4 If a sodium sulphite solution is used for absorption, sulphur dioxide and the sulphite solution can be recovered. Write down the balanced equations and point out possible ...
... atmospheric liquid water pool of 5000 m3 and fully returned on earth as rain, what is the expected pH of the condensed water? 3.4 If a sodium sulphite solution is used for absorption, sulphur dioxide and the sulphite solution can be recovered. Write down the balanced equations and point out possible ...
Microporous polymer beads for chemical
... The obtained polymer beads were further functionalized through conversion of methyl acrylate into the corresponding anion of hydroxamic acid. The hydroxamate anion was chosen as the reactive moiety of the decontamination product due to its high reactivity toward organophosphorus nerve agent and stru ...
... The obtained polymer beads were further functionalized through conversion of methyl acrylate into the corresponding anion of hydroxamic acid. The hydroxamate anion was chosen as the reactive moiety of the decontamination product due to its high reactivity toward organophosphorus nerve agent and stru ...
volume 2 - HotNews
... atmospheric liquid water pool of 5000 m and fully returned on earth as rain, what is the expected pH of the condensed water? ...
... atmospheric liquid water pool of 5000 m and fully returned on earth as rain, what is the expected pH of the condensed water? ...
- Chemistry
... and 0.500 mol of O2(g) – both gases separately at 1 bar pressure – are combined in a vessel such that the total pressure is 1 bar (i.e. 1 ½ × the vessel containing the carbon monoxide), then reacted completely at fixed pressure to form 1 mol CO2(g) at 1 bar. (b) The standard enthalpy change of this ...
... and 0.500 mol of O2(g) – both gases separately at 1 bar pressure – are combined in a vessel such that the total pressure is 1 bar (i.e. 1 ½ × the vessel containing the carbon monoxide), then reacted completely at fixed pressure to form 1 mol CO2(g) at 1 bar. (b) The standard enthalpy change of this ...
Chapter 12 384 12.1 A system is isolated if it exchanges neither
... Since temperature does not change, we can rearrange the equation to: ∆Ereaction ≅∆Hreaction – RT∆(n)(gases) Begin by calculating the change in moles of gases, then use the rearranged equation to determine the ∆Ereaction (a) ∆ngases = 2 – (3 + 1) = –2 mol; 10 − 3 kJ 8.314 J ...
... Since temperature does not change, we can rearrange the equation to: ∆Ereaction ≅∆Hreaction – RT∆(n)(gases) Begin by calculating the change in moles of gases, then use the rearranged equation to determine the ∆Ereaction (a) ∆ngases = 2 – (3 + 1) = –2 mol; 10 − 3 kJ 8.314 J ...
Chemistry Model Question Paper - MCQs Test 2
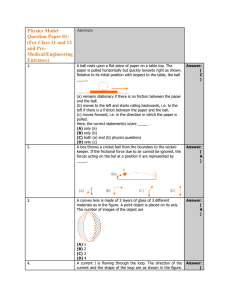
... A ball rests upon a flat piece of paper on a table top. The paper is pulled horizontally but quickly towards right as shown. Relative to its initial position with respect to the table, the ball _____. ...
... A ball rests upon a flat piece of paper on a table top. The paper is pulled horizontally but quickly towards right as shown. Relative to its initial position with respect to the table, the ball _____. ...
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, 3rd Update Edition
... engineering approach to solving process-related problems: breaking a process down into its components, establishing the relations between known and unknown process variables, assembling the information needed to solve for the unknowns using a combination of experimentation, empiricism, and the appli ...
... engineering approach to solving process-related problems: breaking a process down into its components, establishing the relations between known and unknown process variables, assembling the information needed to solve for the unknowns using a combination of experimentation, empiricism, and the appli ...
chapter 4 types of chemical reactions and solution stoichiometry
... unequal sharing of electrons in bonds that results in unequal charge distribution in the overall molecule. Polar molecules have a partial negative end and a partial positive end. These are not full charges as in ionic compounds but are charges much smaller in magnitude. Water is a polar molecule and ...
... unequal sharing of electrons in bonds that results in unequal charge distribution in the overall molecule. Polar molecules have a partial negative end and a partial positive end. These are not full charges as in ionic compounds but are charges much smaller in magnitude. Water is a polar molecule and ...
Preparation and reactions of some lower tungsten halides and
... Conspicuous for their absence among the known halides of tungsten are those of tungsten(III). ...
... Conspicuous for their absence among the known halides of tungsten are those of tungsten(III). ...
Chapter 13 414 13.1 (a) A sand castle represents an ordered
... (b) There is a negative value because of the reduction in number of moles of gaseous substances: 2 moles of gaseous reactants are converted to 1 mole of gaseous products; (c) There is a negative value because of the reduction in number of moles of gaseous substances: 3 moles of gaseous reactants are ...
... (b) There is a negative value because of the reduction in number of moles of gaseous substances: 2 moles of gaseous reactants are converted to 1 mole of gaseous products; (c) There is a negative value because of the reduction in number of moles of gaseous substances: 3 moles of gaseous reactants are ...
A Review of Surface Analysis Techniques for the
... industrial chemical processes, involving the manufacturing of commodity chemicals, pharmaceuticals, clean fuels, etc., as well as pollution abatement technologies, have a common catalytic origin. As catalysis proceeds at the surface, it is of paramount importance to gain insight into the fundamental ...
... industrial chemical processes, involving the manufacturing of commodity chemicals, pharmaceuticals, clean fuels, etc., as well as pollution abatement technologies, have a common catalytic origin. As catalysis proceeds at the surface, it is of paramount importance to gain insight into the fundamental ...
X Science Practice Paper - Brilliant Public School Sitamarhi
... Q 30 Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas? Marks (3) Q 31 You have given three test tubes, one of them contain distilled water and the other two contain an acid solution and a basic solution respe ...
... Q 30 Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas? Marks (3) Q 31 You have given three test tubes, one of them contain distilled water and the other two contain an acid solution and a basic solution respe ...
Quantitative Chemical Analysis
... One of our most pressing problems is the need for sources of energy to replace oil. The chart at the right shows that world production of oil per capita has probably already peaked. Oil will play a decreasing role as an energy source and should be more valuable as a raw material than as a fuel. Ther ...
... One of our most pressing problems is the need for sources of energy to replace oil. The chart at the right shows that world production of oil per capita has probably already peaked. Oil will play a decreasing role as an energy source and should be more valuable as a raw material than as a fuel. Ther ...
Stoichiometry

Stoichiometry /ˌstɔɪkiˈɒmɨtri/ is the calculation of relative quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.Stoichiometry is founded on the law of conservation of mass where the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products leading to the insight that the relations among quantities of reactants and products typically form a ratio of positive integers. This means that if the amounts of the separate reactants are known, then the amount of the product can be calculated. Conversely, if one reactant has a known quantity and the quantity of product can be empirically determined, then the amount of the other reactants can also be calculated.As seen in the image to the right, where the balanced equation is:CH4 + 2 O2 → CO2 + 2 H2O.Here, one molecule of methane reacts with two molecules of oxygen gas to yield one molecule of carbon dioxide and two molecules of water. Stoichiometry measures these quantitative relationships, and is used to determine the amount of products/reactants that are produced/needed in a given reaction. Describing the quantitative relationships among substances as they participate in chemical reactions is known as reaction stoichiometry. In the example above, reaction stoichiometry measures the relationship between the methane and oxygen as they react to form carbon dioxide and water.Because of the well known relationship of moles to atomic weights, the ratios that are arrived at by stoichiometry can be used to determine quantities by weight in a reaction described by a balanced equation. This is called composition stoichiometry.Gas stoichiometry deals with reactions involving gases, where the gases are at a known temperature, pressure, and volume and can be assumed to be ideal gases. For gases, the volume ratio is ideally the same by the ideal gas law, but the mass ratio of a single reaction has to be calculated from the molecular masses of the reactants and products. In practice, due to the existence of isotopes, molar masses are used instead when calculating the mass ratio.