chapter 4 types of chemical reactions and solution
... Data can be imprecise if the measuring device is imprecise as well as if the user of the measuring device has poor skills. Data can be inaccurate due to a systematic error in the measuring device or with the user. For example, a balance may read all masses as weighing 0.2500 g too high or the user o ...
... Data can be imprecise if the measuring device is imprecise as well as if the user of the measuring device has poor skills. Data can be inaccurate due to a systematic error in the measuring device or with the user. For example, a balance may read all masses as weighing 0.2500 g too high or the user o ...
chapter 3 stoichiometry of formulas and equations
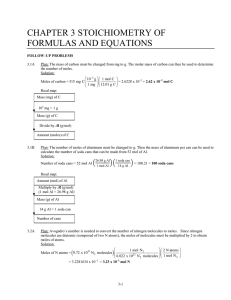
... Initially, Ca and C are balanced. Proceeding to another element, such as N, or better yet the group of elements in NO 3 – gives the following partially balanced equation: 2HNO 3 (aq) + CaCO 3 (s) → CO 2 (g) + H 2 O(l) + Ca(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) Now, all the elements are balanced. c) We are told all the subs ...
... Initially, Ca and C are balanced. Proceeding to another element, such as N, or better yet the group of elements in NO 3 – gives the following partially balanced equation: 2HNO 3 (aq) + CaCO 3 (s) → CO 2 (g) + H 2 O(l) + Ca(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) Now, all the elements are balanced. c) We are told all the subs ...
Chapter 4: Quantities of Reactants and Products
... must add up to the masses of the products, 284.16 g. This looks right. 12. Define the problem: Given the balanced equation for a reaction, identify the stoichiometric coefficients in this equation, and relate the quantity of products to reactants and vice versa. Develop a plan: (a) The law of conser ...
... must add up to the masses of the products, 284.16 g. This looks right. 12. Define the problem: Given the balanced equation for a reaction, identify the stoichiometric coefficients in this equation, and relate the quantity of products to reactants and vice versa. Develop a plan: (a) The law of conser ...
Chapter 4 – Chemical Composition
... for us to see and manipulate. If you could count 1000 water molecules per second for slightly over 20 billion years, you would have counted the molecules in one small drop of water (about 0.020 mL). Instead, because we know the mass of one mole of any substance, we can carefully weigh out an amount ...
... for us to see and manipulate. If you could count 1000 water molecules per second for slightly over 20 billion years, you would have counted the molecules in one small drop of water (about 0.020 mL). Instead, because we know the mass of one mole of any substance, we can carefully weigh out an amount ...
CHAPTER 3 STOICHIOMETRY OF FORMULAS AND EQUATIONS
... molar mass is larger. Balance C: The element on the left (orange) has the higher molar mass because 5 orange balls are heavier than 5 purple balls. Since the orange ball is heavier, its atomic mass is larger, and therefore its molar mass is larger. Balance D: The element on the left (gray) has the ...
... molar mass is larger. Balance C: The element on the left (orange) has the higher molar mass because 5 orange balls are heavier than 5 purple balls. Since the orange ball is heavier, its atomic mass is larger, and therefore its molar mass is larger. Balance D: The element on the left (gray) has the ...
Solutions Manual
... The concept map should explain how to determine the mass of CaCl2 produced from a given mass of HCl. Concept maps will vary, but all should show the use of these conversion factors: the inverse of molar mass, the mole ratio, the molar mass. ...
... The concept map should explain how to determine the mass of CaCl2 produced from a given mass of HCl. Concept maps will vary, but all should show the use of these conversion factors: the inverse of molar mass, the mole ratio, the molar mass. ...
chapter 4 types of chemical reactions and solution stoichiometry
... For covalent compounds, nonzero oxidation states are imaginary charges the elements would have if they were held together by ionic bonds (assuming the bond is between two different nonmetals). Nonzero oxidation states for elements in covalent compounds are not actual charges. Oxidation states for co ...
... For covalent compounds, nonzero oxidation states are imaginary charges the elements would have if they were held together by ionic bonds (assuming the bond is between two different nonmetals). Nonzero oxidation states for elements in covalent compounds are not actual charges. Oxidation states for co ...
chapter 4 types of chemical reactions and solution stoichiometry
... a. The species reduced is the element that gains electrons. The reducing agent causes reduction to occur by itself being oxidized. The reducing agent generally refers to the entire formula of the compound/ion that contains the element oxidized. b. The species oxidized is the element that loses elect ...
... a. The species reduced is the element that gains electrons. The reducing agent causes reduction to occur by itself being oxidized. The reducing agent generally refers to the entire formula of the compound/ion that contains the element oxidized. b. The species oxidized is the element that loses elect ...
CHAPTER 4 SOLUTION STOICHIOMETRY 1 CHAPTER FOUR
... The best way to identify a redox reaction is to assign oxidation states to all elements in the reaction. If elements show a change in oxidation states when going from reactants to products, then the reaction is a redox reaction. No change in oxidation states indicates the reaction is not a redox rea ...
... The best way to identify a redox reaction is to assign oxidation states to all elements in the reaction. If elements show a change in oxidation states when going from reactants to products, then the reaction is a redox reaction. No change in oxidation states indicates the reaction is not a redox rea ...
Chapter 4
... The best way to identify a redox reaction is to assign oxidation states to all elements in the reaction. If elements show a change in oxidation states when going from reactants to products, then the reaction is a redox reaction. No change in oxidation states indicates the reaction is not a redox rea ...
... The best way to identify a redox reaction is to assign oxidation states to all elements in the reaction. If elements show a change in oxidation states when going from reactants to products, then the reaction is a redox reaction. No change in oxidation states indicates the reaction is not a redox rea ...
Chapter 4 Solution Manual
... Plan: Compounds that are soluble in water tend to be ionic compounds or covalent compounds that have polar bonds. Many ionic compounds are soluble in water because the attractive force between the oppositely charged ions in an ionic compound are replaced with an attractive force between the polar wa ...
... Plan: Compounds that are soluble in water tend to be ionic compounds or covalent compounds that have polar bonds. Many ionic compounds are soluble in water because the attractive force between the oppositely charged ions in an ionic compound are replaced with an attractive force between the polar wa ...
Chapter 13 414 13.1 (a) A sand castle represents an ordered
... 13.17 (a) Both are ionic solutions, but MgCl2 produces three moles of ions per mole of substance, while NaCl produces two moles of ions per mole of substance, so MgCl2 has the larger molar entropy; (b) Both are ionic solids, but HgS has a higher molar mass than HgO, so HgS has the larger molar entro ...
... 13.17 (a) Both are ionic solutions, but MgCl2 produces three moles of ions per mole of substance, while NaCl produces two moles of ions per mole of substance, so MgCl2 has the larger molar entropy; (b) Both are ionic solids, but HgS has a higher molar mass than HgO, so HgS has the larger molar entro ...
chapter 5 gases and the kinetic
... using M = mRT/PV. The problem also states that the gas is a hydrocarbon, which by, definition, contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms. We are also told that each molecule of the gas contains five carbon atoms so we can use this information and the calculated molar mass to find out how many hydrogen ...
... using M = mRT/PV. The problem also states that the gas is a hydrocarbon, which by, definition, contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms. We are also told that each molecule of the gas contains five carbon atoms so we can use this information and the calculated molar mass to find out how many hydrogen ...
Introductory Chemistry
... 10. Answer depends on student response. A quantitative observation must include a number. For example, “There are two windows in this room.” represents a quantitative observation, but, “The walls of this room are yellow.” is a qualitative observation. 12. A natural law is a summary of observed, meas ...
... 10. Answer depends on student response. A quantitative observation must include a number. For example, “There are two windows in this room.” represents a quantitative observation, but, “The walls of this room are yellow.” is a qualitative observation. 12. A natural law is a summary of observed, meas ...
ch15
... Q12. A solution of nitric acid is placed in a burette in order to determine its concentration. 20.00 mL of 0.099 27 M potassium hydroxide is placed, using a pipette, in a conical flask. When the equivalence point was reached, 18.26 mL of the acid was delivered by the burette. Calculate the concentra ...
... Q12. A solution of nitric acid is placed in a burette in order to determine its concentration. 20.00 mL of 0.099 27 M potassium hydroxide is placed, using a pipette, in a conical flask. When the equivalence point was reached, 18.26 mL of the acid was delivered by the burette. Calculate the concentra ...
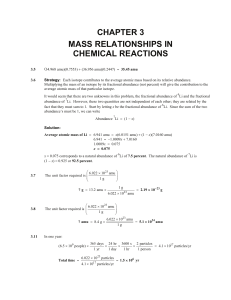
CHAPTER 3 MASS RELATIONSHIPS IN CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... Strategy: We are given grams of ethane and asked to solve for molecules of ethane. We cannot convert directly from grams ethane to molecules of ethane. What unit do we need to obtain first before we can convert to molecules? How should Avogadro's number be used here? Solution: To calculate number of ...
... Strategy: We are given grams of ethane and asked to solve for molecules of ethane. We cannot convert directly from grams ethane to molecules of ethane. What unit do we need to obtain first before we can convert to molecules? How should Avogadro's number be used here? Solution: To calculate number of ...
Chapter 15 Calculations in chemistry: stoichiometry
... Q12. A solution of nitric acid is placed in a burette in order to determine its concentration. 20.00 mL of 0.099 27 M potassium hydroxide is placed, using a pipette, in a conical flask. When the equivalence point was reached, 18.26 mL of the acid was delivered by the burette. Calculate the concentra ...
... Q12. A solution of nitric acid is placed in a burette in order to determine its concentration. 20.00 mL of 0.099 27 M potassium hydroxide is placed, using a pipette, in a conical flask. When the equivalence point was reached, 18.26 mL of the acid was delivered by the burette. Calculate the concentra ...
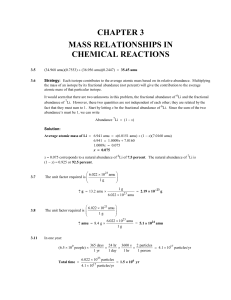
CHAPTER 3 MASS RELATIONSHIPS IN CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... Strategy: We are given grams of ethane and asked to solve for molecules of ethane. We cannot convert directly from grams ethane to molecules of ethane. What unit do we need to obtain first before we can convert to molecules? How should Avogadro's number be used here? Solution: To calculate number of ...
... Strategy: We are given grams of ethane and asked to solve for molecules of ethane. We cannot convert directly from grams ethane to molecules of ethane. What unit do we need to obtain first before we can convert to molecules? How should Avogadro's number be used here? Solution: To calculate number of ...
Chapter 4 - Chemistry
... (a) is a strong electrolyte. The compound dissociates completely into ions in solution. (b) is a nonelectrolyte. The compound dissolves in water, but the molecules remain intact. (c) is a weak electrolyte. A small amount of the compound dissociates into ions in water. When NaCl dissolves in water it ...
... (a) is a strong electrolyte. The compound dissociates completely into ions in solution. (b) is a nonelectrolyte. The compound dissolves in water, but the molecules remain intact. (c) is a weak electrolyte. A small amount of the compound dissociates into ions in water. When NaCl dissolves in water it ...
endmaterials
... 16. How many moles of ammonium ions are in 4.50 mol (NH4)2CO3? 17. Determine the molar mass of silver nitrate. 18. Calculate the molar mass of acetic acid (CH3COOH). 19. Determine the mass of 8.57 mol of sodium dichromate (Na2Cr2O7). 20. Calculate the mass of 42.5 mol of potassium cyanide. 21. Deter ...
... 16. How many moles of ammonium ions are in 4.50 mol (NH4)2CO3? 17. Determine the molar mass of silver nitrate. 18. Calculate the molar mass of acetic acid (CH3COOH). 19. Determine the mass of 8.57 mol of sodium dichromate (Na2Cr2O7). 20. Calculate the mass of 42.5 mol of potassium cyanide. 21. Deter ...
Appendices
... 16. How many moles of ammonium ions are in 4.50 mol (NH4)2CO3? 17. Determine the molar mass of silver nitrate. 18. Calculate the molar mass of acetic acid (CH3COOH). 19. Determine the mass of 8.57 mol of sodium dichromate (Na2Cr2O7). 20. Calculate the mass of 42.5 mol of potassium cyanide. 21. Deter ...
... 16. How many moles of ammonium ions are in 4.50 mol (NH4)2CO3? 17. Determine the molar mass of silver nitrate. 18. Calculate the molar mass of acetic acid (CH3COOH). 19. Determine the mass of 8.57 mol of sodium dichromate (Na2Cr2O7). 20. Calculate the mass of 42.5 mol of potassium cyanide. 21. Deter ...
Chapter 12 384 12.1 A system is isolated if it exchanges neither
... 12.37 The formation of a solid from ions in solution involves two opposing energy effects. Energy is released because of the coulombic attraction between cations and anions, but energy is absorbed to overcome the ion-dipole attractions between ions and water molecules. Solid formation is endothermic ...
... 12.37 The formation of a solid from ions in solution involves two opposing energy effects. Energy is released because of the coulombic attraction between cations and anions, but energy is absorbed to overcome the ion-dipole attractions between ions and water molecules. Solid formation is endothermic ...
Chapter 3 - Chemistry
... Strategy: We are asked to solve for the number of N, C, O, and H atoms in 1.68 104 g of urea. We cannot convert directly from grams urea to atoms. What unit do we need to obtain first before we can convert to atoms? How should Avogadro's number be used here? How many atoms of N, C, O, or H are in ...
... Strategy: We are asked to solve for the number of N, C, O, and H atoms in 1.68 104 g of urea. We cannot convert directly from grams urea to atoms. What unit do we need to obtain first before we can convert to atoms? How should Avogadro's number be used here? How many atoms of N, C, O, or H are in ...
Chapter 15 Calculations in chemistry: stoichiometry
... grams and M is the molar mass. A periodic table is used to calculate the molar masses of NaOH = 40.0 g mol–1. The volume of H2SO4 is found by using n = cV, where c is the concentration in mol L–1 and V is the volume in litres. n ( H 2 SO 4 ) 1 ...
... grams and M is the molar mass. A periodic table is used to calculate the molar masses of NaOH = 40.0 g mol–1. The volume of H2SO4 is found by using n = cV, where c is the concentration in mol L–1 and V is the volume in litres. n ( H 2 SO 4 ) 1 ...
Chapter 4 MATERIAL BALANCES AND APPLICATIONS
... 1. Draw and label the process flow chart (block diagram). When labeling, write the values of known streams and assign symbols to unknown stream variables. Use the minimum number possible of symbols. 2. Select a basis of calculation. This is usually the given stream amounts or flow rates, if no given ...
... 1. Draw and label the process flow chart (block diagram). When labeling, write the values of known streams and assign symbols to unknown stream variables. Use the minimum number possible of symbols. 2. Select a basis of calculation. This is usually the given stream amounts or flow rates, if no given ...