* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Vesicular monoamine transporter wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
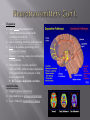
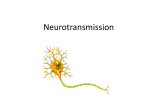
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
chemicals released by vesicles in sending neuron travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on receiving neuron 2 TYPES = EXCITATORY = stimulate the brain, increase the likelihood that the neuron will fire an action potential INHIBITORY = calm the brain, balance mood & are depleted when excitatory are overactive Neurotransmitters bind to the receptors of the receiving neuron in a “key-lock mechanism”. Serotonin various functions = body temp., sleep, mood, appetite, and pain Low levels =implicated in depression & probs with immune syst. High = Serotonin Syndrome stimulant medications or caffeine in your daily regimen can cause a depletion of serotonin Norepinephrine (AKA Noradreneline) Prepares you for action important for attentiveness, emotions, sleeping, dreaming, and learning causes blood vessels to contract & heart rate to increase GABA Gamma-Amino Butyric Acid An inhibitory neurotransmitter “nature’s VALIUM-like substance” Related probs = anxiety, seizures, Huntington’s disease Valium and similar antianxiety drugs work at GABA synapses Dopamine main focus neurotransmitter Affects neurons associated with voluntary movement role in learning, memory, and emotions Loss of dopamine-producing cells = Parkinson’s Disease Excess = focusing issues, less motivation, schizophrenia Stimulants (ex: cocaine, meds for ADD/ADHD, caffeine) cause dopamine to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease Endorphins linked to pain control and to pleasure Reduce pain by inhibiting or “turning down” neurons that transmit pain information natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters “morphine within” Dopamine pathways are involved with diseases such as Parkinson’s disease caused by a deterioration of brain neuron’s that produce dopamine (it is still unknown why this occurs) Although not the sole cause of schizophrenia, dopamine unbalance is consistently seen found in patients with schizophrenia Drugs that prevent dopamine from binding to receptors reduce the symptoms of schizophrenia Agonist Increases production Activates the neuron receptor that it attaches to Antagonist Decreases production Deactivates the neuron receptor that it attaches to