* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sequencing a genome
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
DNA barcoding wikipedia , lookup
Adeno-associated virus wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Copy-number variation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
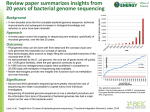
Sequencing a genome (a) outline the steps involved in sequencing the genome of an organism; (b) outline how gene sequencing allows for genomewide comparisons between individuals and between species; Genome size & complexity Increasing complexity Viruses Bacteria Protozoa Inverterbrates Issues for consideration when sequencing: Mammals Plants Issues for consideration when annotating: DNA source Genome size Genome size Repeat content Repeat content Splicing Duplications and inversions Genefinding resources Likely comparator species Genome sequencing Sequencing involves: DNA fragmenting into small pieces Sequence determination Assembly into large contiguous sequences Problems occur: Cloning steps Bacterial transformation and amplification Sequencing chemistry Assembly of repetitive regions Sequencing a Genome 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Sequence coverage Most genome sequences are not complete (not finished). Whole Genome Shotguns are referred to as having an X-fold coverage. Low coverage (2x) is sufficient for gene discovery and some regulatory element identification. High coverage (6x) is good for gene annotation. There will still be some missing genes. Finished sequence has no gaps and is presumed to contain all genes. The sequencing of the human genome Animation of genome sequencing Some current and potential applications of genome research include Molecular medicine Energy sources and environmental applications Risk assessment Bioarchaeology, anthropology, evolution, and human migration DNA forensics (identification) Agriculture, livestock breeding, and bioprocessing Detail of each bullet point