* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CSCE590/822 Data Mining Principles and Applications
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA barcoding wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
CSCE555 Bioinformatics
Lecture 2
Meeting: MW 4:00PM-5:15PM SWGN2A21
Instructor: Dr. Jianjun Hu
Course page: http://www.scigen.org/csce555
University of South Carolina
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
2008 www.cse.sc.edu.
Roadmap
DNA, Chromosomes, Genomes
Genome Sequencing and whole genomes
DNA Sequence Representation, Models
Sequence Retrieval, Manipulation
Basic Analysis and Questions of Genomes
Summary
5/23/2017
2
Tools to Learn Concepts Quickly
Wikipedia.org
◦ Search “Genome” bringing up many related
information
◦ In google, type “keywards wiki”
Google search tips
◦ Find info from university websites
Genome, site:edu
◦ Find info as powerpoint files
Genome, tutorial, filetype:ppt
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic
acid (DNA) is a
nucleic acid that
contains the genetic
instructions used in
the development and
functioning of all
known living
organisms.
DNA is a long polymer of simple units
called nucleotides
Bases
A: adenosine
C: cytidine
G: guanosine
T: thymidine
Backbone:
sugars and phosphate groups
Microbial Genome: Clostridium sp.
OhILAs
CTGCTGTACTAGGATGCTGGTGGAGAGAGCTGCATATAAATCTTTGAGAGATGCACCAAG
AATCACCATCATGGTTTCCGCCATAGGGGCTTCTTTTTTTATTCAAAATCTTGCCATTGT
TTTATTTGGTGGTAGACCGAAAACTGTTCCAACGGTGGAGGTATTGTCCGGGGTGATAAA
GCTGGGGTCCGTATCTCTACAAAGGCTGACCTTAGTGATTCCAGTAGTAACCATACTGCT
ATTATTTCTTTTGATGTTTTTAGTGAACCAAACGAAAACTGGAATGGCAATGCGTGCCGT
ATCCAAGGACTATGAAACCGCGCGGCTTATGGGAATTGACGTCAATAAAATTATTACCAT
AACCTTTGGTATTGGCTCTGCTCTGGCAGCTATTGGTGGCATCATGTGGGGCGCAAAATT
TCCTAAAATAGACCCTTTTGTTGGGACTATGCCGGGTATTAAATGCTTTATTGCTGCAGT
TCTAGGTGGAATCGGAAACATTCCCGGTGCAGTAATCGGGGGGTTCATCTTAGGGATTGG
AGAGATTATGCTCATTGCTTTTCTACCGAGCCTAACTGGCTATCGAGATGCCTTTGCTTT
CATACTACTGATTATCATTCTACTGTTTAAGCCAACAGGAATCATGGGTGAAAAAATTGC
GGAGAAGGTGTAGACGATGAAAAAGAAAAATACCATATTAACTGGATTAGCAGTATTGCT
TTTATTGATTTATTTGATTTATGCAAATAAGAATTATGATTCTTATAAAATTAGAGTTCT
AAATCTATGTGCAATTTATGCTGTATTGGGACTCAGTATGAATTTGATCAATGGATTTAC
AGGTTTATTTTCCCTTGGACATGCAGGTTTTATGGCAGTAGGTGCCTATACTACCGCTCT
TCTGACCATGACACCGCAAAGTAAGGAGGCAACATTCTTCTTAGTGCCCATTGTAGAGCC
TTTGGCTAAAATTCAGCTTCCTTTTTTTGTGGCACTGATCATCGGTGGACTACTTTCAGC
AATGGTGGCATTTTTAATCGGTGCACCGACTTTAAGGCTGAAGGGCGATTATTTAGCCAT
Complementary Base Pairing:
AT
Write a program to export
CG
complementary sequence?
Genome of organisms
genome of an
organism is a
complete DNA
sequence of one set
of chromosomes
Sequencing: Basic Ideas
Current lab techniques can sequence small (say 700 base pairs) DNA
pieces.
◦ Use restriction enzymes to cut DNA pieces
◦ Sort pieces of different sizes using gel electrophoresis and use the sorting to
read them
Mapping and Walking
◦ Sequence one piece, get 700 letters, make a primer that allowed you to read the
next 700, and work sequentially down the clone
◦ Estimate for human genome sequencing using this method: 100 years
Shotgun sequencing (introduced by Sanger et al. 1977) for sequencing
genomes
◦ Obtain random sequence reads from a genome
◦ Assemble them into contigs on the basis of sequence overlaps
Straightforward for simple genomes (with no or few repeat sequences)
Merge reads containing overlapping sequence
Shotgun sequencing is more challenging for complex (repeat-rich)
genomes: two approaches
How Sequencing Works
Beckman CEQ 8000
Sequencing small DNA pieces
G
G
A
T
--------------
A
--------------
C
--------------
T
--------------
T
--------------
A
G
--------------
--------------
T
--------------
A
--------------
C
--------------
A
--------------
G
--------------
G
--------------
A
--------------
A
--------------
A
--------------
C
--------------
T
G
C
---------------------------
Use DNA cloning or PCR to make
multiple copies.
Put in 4 testtubes marked G, A, T and
C
In testtube G use restriction enzymes
that cuts at G.
Do the above step for the other
testubes.
Use gel electrophoresis separately for
the content in each testtube.
The data results in the table on the
left.
Reading the table we get G has
lengths 1, 7, 12, 13, 19; A has lengths 2,
6, 8, 11, 14,15,16; T has length 4, 5, 9,
18 and C has length 3, 10, 17.
This gives us the sequence.
Methods for very large scale sequencing
A hierarchical approach
◦ Map on a large scale (physical mapping), sequence
specific clones whose position in the genome is
known
Shot gun sequencing
◦ “Tear up” the genome and sequence random
fragments until it is done
Sequence tagged connectors (STC)
◦ Sequence the ends of many clones and use this info
to pick overlapping clones
“Shotgun” sequencing
Copy
Clone to sequence
Sequence and “assemble”
….GTCTACCTGTACTGATCTAGC...
…. CCTGTACTGATCTAGCATTA...
…. GTACTGATCTAGCATTACG...
Subclone
Emerging Sequence Methods
Sequencing by
Hybridization (SBH).
Mass
Spectrophotometric
Sequences.
Direct Visualization of
Single DNA Molecules
by Atomic force
Microscopy (AFM )
Single Molecule
Sequencing
Techniques
Single nucleotide
Cutting
Nanopore sequencing
Readout of Cellular
Gene Expression
Whole Genomes of Species
Bacterial Genomes
Eukaryotic Genomes
Human Genome Project
Other Animal and Plant Genomes
Model Genomes
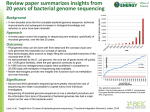
The genomes of more than 180 organisms
have been sequenced since 1995
http://www.genomenewsnetwork.org/resour
ces/sequenced_genomes/genome_guide_
p1.shtml
Sizes of Genomes
You will learn to download all these
genomes into your computer’s
harddrive
Refer to Table 1.1 Page 2 of Intro
to Comp Genomics book.
Roadmap
DNA, Chromosomes, Genomes
Genome Sequencing and whole genomes
DNA Sequence Representation, Models
Sequence Retrieval, Manipulation
Basic Analysis and Questions of Genomes
Summary
5/23/2017
15
DNA Sequence Representation
DNA Sequence: a string of letters with
alphabet {A, C, G, T}
Protein sequence: a string of amino acids
with alphabet
{ARNDCEQGHILKMFPSTWYV}
◦ 20 standard amino acids
Genetic code:
Genetic Code: Condon
DNA (ATCG)
RNA (AUCG)
Three bases of DNA
encode an amino
acid
Genetic Code with Degeneracy
Representation of Sequences
Single DNA sequence
◦ ATCCTTAAGGAAA
Multiple sequences with similarity
◦
◦
◦
◦
◦
Regular Expression
ATAAA
ACAAAA
ATAAAAAA
A[TC]A+
Representation of Sequences
Probablistic Model: Position-specific
scoring matrices (PSSM)
Representation of Sequence:
FASTA format
text-based format for representing either
nucleic acid sequences or peptide
sequences,
allows for sequence names and comments
to precede the sequences.
Roadmap
DNA, Chromosomes, Genomes
Genome Sequencing and whole genomes
DNA Sequence Representation, Models
Sequence Retrieval, Manipulation
Basic Analysis and Questions of Genomes
Summary
5/23/2017
22
Sequence Retrieval, Manipulation
Where to download genome/sequence
data
◦ Online databases: EMBL, GenBank
◦ Entrez cross-database search (life science
search engine)
◦ Goolge -
Example: Download H. influenzae
Genome
First bacterial genome: H. influenzae,
1830Kb
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez
NC_007146
LinksHaemophilus influenzae 86-028NP, complete genome
DNA; circular; Length: 1,914,490 nt
Replicon Type: chromosome
Created: 2005/06/27
Genome Information of H.
influenzae
Download the Complete Genome
Sequence in Fasta Format
Roadmap
DNA, Chromosomes, Genomes
Genome Sequencing and whole genomes
DNA Sequence Representation, Models
Sequence Retrieval, Manipulation
Basic Analysis and Questions of Genomes
Summary
5/23/2017
28
Simple Questions and Analysis of
Genome Sequence
Frequencies of Bases A/C/G/T by simple
counting
Sliding windows to check local density
AT AG AC TA TG TC
K-mers frequent/unusual words
◦ 2-mers AT AG AC TA TG TC etc.
◦ 3-mers
Genomic landscape: GC
content analysis
The overall GC content of the human
genome is 41%.
A plot of GC content versus number of
20 kb windows shows a broad profile
with skewing to the right.
Page 627
GC content of the human genome: mean 41%
Source: IHGSC (2001)
Fig. 17.15
Page 628
Genomic landscape: CpG islands
Dinucleotides of CpG are under-represented in genomic
DNA, occuring at one fifth the expected frequency.
CpG dinucleotides are often methylated on cytosine (and
subsequently may be deamination to thymine).
Methylated CpG residues are often associated with housekeeping genes in the promoter and exonic regions.
Methyl-CpG binding proteins recruit histone deacetylases
and are thus responsible for transcriptional repression.
They have roles in gene silencing, genomic imprinting, and Xchromosome inactivation.
Broad genomic landscape: CpG
islands
Findings:
◦ 50,267 CpG islands in human genome
◦ 28,890 after masking repeats with
RepeatMasker
◦ 5-15 CpG islands per megabase
◦ (about <40 genes per megabase)
Summary
DNA, Chromosome, Genome
Sequence models
Sequence database, retrieval
Whole genome sequence analysis
Slides Credits
Slides in this presentation are partially
based on the work of slides from
Internet.