* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Synaptic Plasticity
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Perceptual learning wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
State-dependent memory wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Concept learning wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Memory consolidation wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
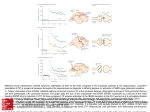
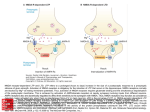
synaptic plasticity Basic Neuroscience NBL 120 classical conditioning CS (neutral) - no response US - UR After pairing: CS - CR associative learning ability to learn the relationship between different stimuli / events so that we can make reasonable predictions if we are faced with a certain situation learning & memory => good addiction => bad learning & memory in taxi drivers PET study during recall of London route (Maguire et al, 1997) place cells some pyramidal cells in the hippocampus have preferred spatial orientations fire in bursts (O’Keefe & Dostrovsky, 1971) how is a synapse plastic? synapses “remember” previous activity short-term, e.g. post-tetanic potentiation at the nmj control motor neuron motor neuron pre musclemuscle nmj time post Hebbian learning longer term plasticity Hebbian learning Hebb (1949) hypothesized that “ if one neuron frequently takes part in exciting another, some growth process or metabolic change takes place in one or both cells and the strength of their connection increases ” hippocampal “integrated circuit” Johnson & Wu (1995) in reality….. after before amplitude first demonstration of LTP high-frequency train rapid induction lasts weeks in vivo time (hrs) Bliss & Lomo (1973) properties of LTP cellular mechanisms underlying LTP induction maintenance excitatory synaptic transmission NMDA vs non-NMDA synaptic transmission AP5 control AP5 LTP depends specifically on NMDA receptor activation AP5 prevents high frequency-induced LTP (Collingridge et al, 1983) what is special about NMDA receptors? voltage-gated channels: voltage ligand-gated channels: transmitter NMDA receptors: both Mg+ out +++ Mg+ --- in +-+ NMDA receptor: a molecular switch co-incidence detector requires both presynaptic activity (glutamate) and postsynaptic depolarization (relieve Mg block) satisfies Hebbian co-incidence rules explains LTP properties: specificity associativity / co-operativity spatial/temporal requirements how does the NMDA receptor cause a change in synaptic strength? synaptic transmission is unreliable increased transmitter release altered or new receptors new synapses NMDA receptors, hippocampus and LTP learning and memory NMDA receptor-dependent learning spatial memory task visual task “Morris” water maze Morris et al (1990) LTP and learning LTP decay saturation of LTP prevents learning a new spatial task new learning can occur after LTP decay Castro et al (1989) a natural LTP? animals raised in a complex environment show enhanced synaptic responses in the hippocampus Sharp et al (1985) hippocampus = temporary memory storage new patterns stored rapidly and transiently gradual transfer to neocortex long-term storage with reduced interference diffuse storage in cortex? computational theories Marr (1970’s) sensory input to neocortex stored by association repetition - association partial pattern recall addiction - definition compulsive use / abuse of a drug despite adverse consequences recollections of an addict: electrical self-stimulation Skinner-box lever-press > reward rate reward “pleasure centers” “a hungry animal often ignored available food in favor of the pleasure of stimulating itself electrically .... 2000 times per hour for 24 consecutive hours” (Olds 1956) where are the pleasure centers? medial forebrain bundle VTA - Nucleus Accumbens (after Koob 1992) dopamine DA neurons and reward (Schultz et al, 1993) drug abuse is a form of associative learning associated cues could trigger “craving” nicotine is continuously paired with taste and smell of cigarettes heroin or other drug use may be associated with a specific setting evidence…………. predicting reward VTA DA response becomes associated with the sound cue i.e. DA response predicts reward learning what happens to DA in addicts? displacement of [11C]raclopride binding by DA release PET scan MP = methylphenidate “RITALIN” “craving” (Volkow et al, 1997) associations - summary synaptic plasticity hippocampus / cortex NMDA receptor - coincidence detector Mg2+ & Ca2+ addiction midbrain - VTA / Nucleus Accumbens Dopamine predictive cues in theory….. (from McNaughton & Morris, 1987)