* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Signal learning
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
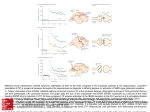
English Programm 2009/10 Neurobiology of Learning Bottom-up: Neuronal mechanisms of learning Classical Conditioning Conditioning Typ S „Signal learning“ Unconditioned Stimulus UCS UR Unconditioned Reaction Iwan Petrowitsch Pawlow (1849-1936) Inhibition: Conditioned Stimulus Conditioned Stimulus CS CS Conditioned Stimulus CR CS CR Unconditioned Reaction Conditioned Reaction UR UCS Unconditioned Reaction Unconditioned Stimulus Lack of Reinforcement results in fading of the reaction Inhibiton is an active process Reaction CS CR Trial Spontaneous Recovery Axiety can be seen as a conditioned emotion and strategies of Pawlow´s theory can be applied: Behavior Therapy John B. Watson (1878-1950) Bliss & Lomo (1973): LTP First observation of facilitation of synaptic transmission after high frequency stimulation of the presynaptic neuron. Long-term potentiation LTP remains stable for many weeks Hebb postulate for learning (1949): Facilitation of synaptic transmission is the neuronal basis of learning NMDA receptor responds maximally if: NMDA receptor [N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor] Glutamat binds to it Neuron is depolarized Maximal influx of Na + and Ca+ + ions triggering enzymes [protein kinases] Evidence that LTP is involved in learning: The critical factor is the co-occurence of firing in presynaptic and postsynaptic cells Reconfirmed for NMDA by Bi & Poo 2001 LTP triggers structural changes: • Increased number of synapses LTP occurs at synapses participating in learning • Increased size of synapses Conditioning produces LTP-like changes • Increased number of NMDA receptors Mutant mice with little LTP have learning difficulties E. R. Kandel Nobelpreis 2000 The molecular biology of memory storage: A dialogue between gens and synapses. [Science 2001] Their functions are well known Aplysia has 20 000 neurons only Sea-slug Aplysia Kandels modell for learning was the withdrawl reflex of the gill of Aplysia The motoneuron L7 controls quick withldraw of the gill Nucleus Sensory neuron Serotonin Receptor Motor neuron Sipho-System: 24 sensory neurons connected with 6 motoneurons controlling the withdrawl of the gill New connections are seen after application of Serotonin only Reinforcement by increased release of glutamat Basis of short term memory is an increased release of neurotransmitter. Tissue cultures for simple learning networks New synaptic junctions Information from DNA Anatomical changes Long term memory is based on new synaptic junctions Why growth takes place in activated synapses only was studed on branched axons Serotonin cAMP Proteinkinases A activates protein CREB 1 inducing gene expression Serotonin cAMP MAF-Kinases deactivates protein CREB 2 gen-expression Gen-expression results in production of (silent) mRNA The prionlike protein CPEB [cytoplasmatic polyadenylation element-binding Protein] converts recessive into dominant mRNA. Only application of serotonin effected synaptic modifications Proteins reach all synapses. Only in serotonin-stimulated regions mRNA is activated and growth takes place. Somatosensory representation in the Owl Monkey Neuronal Plasticity: Structual changes can even alter the size of cortical projection areas [M. M. Merzenich 1990] Sensibility training for several weeks Somatosensory areas before (l) and after (r) training Formation of new nerve cells takes place also postnatal. First discovered by Nottebohm in the brain of birds. Fernando Nottebohm: New nerve cells follow certain glial fibres Instrumental Conditioning Similar effects were recently observed also in the human brain Edward L. Thorndike (1874-1949) Burrhus F. Skinner (1904-1990) Positive Reinforcement Conditionierung Typ R „Reaction-Learning“ Spontaneous Behavior Increase of Probability Spontaneous Behavior Learning by Reinforcement Negative Reinforcement Fading in Fading out Olds & Milner Self-Stimulation Positive Negative Reward Centers Decrease of Probability Top-down: Psychology of cognitive learning The mesotelencephalic dopamine system: Nigrostriatal pathway (green) and mesocorticolimbic pathway (red) Hermann Ebbinghaus Material Curve of forgetting “Overlearning“ does not increase long term memory Time Material Material 5 10 20 . . . Memory interference Time Time Control Hubert Rohracher: Retroactive Inhibition Consolidation “The brain learns longer than consciousness” Proactive inhibition Postmental excitations Papez Circle – Limbic System Hippocampus Amygdala Fornix Gyrus cinguli Corpus mamillare