* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structure & Function
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
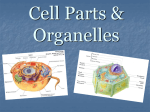
Cell Structure & Function Cell Theory • All living things are made of cells • Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in organisms • Cells only come from pre-existing cells • Schleiden, Schwann, & Virchow Cell Diversity • Differ in size, shape, & function • Shape determines function Prokaryotes • “Pro-” = before • “-karyote” = nucleus • No nucleus • No membrane-bound organelles • Unicellular • Found in Kingdoms Archaebacteria and Eubacteria Eukaryotes • “Eu-” = true (true nucleus) • Have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles • Unicellular or Multicellular • More complex than prokaryotes • Found in Kingdoms Animalia, Plantae, Protista, & Fungi Cell Membrane • Surrounds the entire cell • Controls what enters and leaves the cell • Made of: • Phospholipids (heads and tails) • Proteins • Carbohydrates • Cholesterol • Steroids Nucleus • Control center of the cell (“brain”) • Surrounded by a membrane (nuclear envelope) • Membrane contains pores (communication) • Houses DNA (chromatin) • Contains nucleolus (where RNA is made) Cytoplasm • Includes everything between the cell membrane and the nucleus • Jelly-like • Made up of organelles and cytosol (water and proteins) Ribosomes • Site of protein synthesis • Made up of rRNA and proteins • Not surrounded by a membrane • Located in the cytoplasm or attached to rough ER Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum • “Roadway” of the cell • Helps in making and transporting proteins • Ribosomes are on the surface - give “rough” appearance • Endoplasmic Reticulum = ER Smooth ER • “Roadway” of the cell • Helps cell to break down poisons, waste, and toxins • Helps cell process lipids and carbohydrates • ER network (rough & smooth) connects nucleus and cell membrane Golgi Body • Modifies, packages, and secretes cell products • Consists of flattened stacks of cisternae • Receives products made by the ER Lysosomes • Contain hydrolytic enzymes to digest materials for the cell • Surrounded by a single membrane • Formed from ends of Golgi body that pinch off • Not found in plant cells Mitochondria • Site of cellular respiration • Energy (ATP - adenosine triphosphate) is made • Have their own DNA • Inner membrane is folded (cristae) Chloroplast • Type of plastid (pigment containing organelle) • Stacked inner membranes called thylakoids used to trap sunlight for photosynthesis • Contain chlorophyll (green) • Have their own DNA • Found in plants, seaweed, and, algae • Other plastids can be red, orange, and Vacuole • Largest organelle in plant cells • Hold water and help cell keep its shape (wilt) • Storage area for water, proteins, ions, and glucose • Animal vacuoles are smaller and used for digestion Cytoskeleton • Helps cell maintain shape • Helps move organelles around the cell (tracks) • Types: • Microfilaments • Microtubules Centrioles • Made of microtubules • Assist in cell division (mitosis) • Not found in plant cells Cilia & Flagella • Cilia - hair-like projections on a cell made of bundles of microtubules • Flagella - whip-like tails of microtubules • Both help with cell movement Cell Wall • Non-living protective layer around plant, fungal, and bacterial cells • Plant cell walls are made of cellulose Multicellular Organization • Cells are specialized for their functions • Levels of organization: • Cell • Tissue • Organ • Organ System • Organism