* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Structure of the Cell Membrane
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
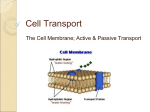
Cellular Transport Notes About Cell Membranes 1.All cells have a _____ _________ 2.Functions: a.Controls what enters and exits the cell ___ _________________ called ____________ b.Provides _________ and _______ for the cell TEM picture of a real cell membrane. About Cell Membranes (continued) 3.Structure of cell membrane Lipid Bilayer -2 layers of _____________ a.Phosphate head is _____ (________ - water loving) b.Fatty acid tails ________ (__________ - water fearing) c._________ embedded in membrane Phospholipid Lipid Bilayer Polar heads _____________ love water ______of the & dissolve. cell membrane Non-polar tails hide from water. Carbohydrate cell markers Proteins Membrane movement animation About Cell Membranes (continued) • 4. Cell membranes have ______(holes) in it a.____________ ___________: Allows some molecules in and keeps other molecules out b.The ___________ helps it be selective! Pores Structure of the Cell Membrane Outside of cell Proteins Lipid Bilayer Transport Protein Animations of membrane Go to structure Section: Carbohydrate chains Phospholipids Inside of cell (cytoplasm) Types of Cellular Transport •Animations of Active Transport & Passive Transport • Weeee!! ! Passive Transport cell ________ use energy 1. _________ 2. _________ _________ 3. _________ • high low Active Transport cell ____ use energy 1. _______ ________ 2. ___________ 3. ___________ This is gonna be hard work!! high low Passive Transport • • • cell _____ ___ _________ molecules move __________ Molecules spread out from an area of _____ concentration to an area of _____concentration. • (HighLow) • Three types. . . 3 Types of Passive Transport 1. Diffusion 2. Facilitative Diffusion – diffusion with the help of _________ _________ 3. Osmosis – diffusion __ _______ Passive Transport: 1. Diffusion Simple Diffusion Animation 1. Diffusion: ______ movement of particles from an area of ______ concentration to an area of ____ concentration. (High to Low) • Diffusion continues until all molecules are _____ _______ (__________ is reached)-Note: molecules will still _____ ______ but stay spread out. http://bio.winona.edu/berg/Free.htm Passive Transport: 2. Facilitated Diffusion A 2. Facilitated diffusion: diffusion of specific particles ______ _______ ________ found in the _________ a.Transport Proteins are ________ – they “select” only certain molecules to cross the membrane b.Transports _______ or ________ molecules Facilitated diffusion (Channel Protein) Carrier Protein B Diffusion (Lipid Bilayer) Passive Transport: 2. Facilitated Diffusion Glucose molecules Cellular Transport From aHigh Concentration High • Channel Proteins animations Cell Membrane Low Concentration Through a Go to Section: Transport Protein Protein channel Low Passive Transport: 3. Osmosis • 3.Osmosis: diffusion of _______ through a selectively permeable membrane • Water moves from _____ to ____ concentrations Osmosis animation •Water moves freely through pores. •Solute (green) too large to move across. Effects of Osmosis on Life • Osmosis- diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane • Water is so small and there is so much of it the cell can’t control it’s movement through the cell membrane. • Hypertonic Solution Osmosis Animations for isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions Hypertonic: The solution has a ______ concentration of solutes and a ______ concentration of water than inside the cell. (High _______; Low _______) shrinks Result: Water moves from ______ the cell _____ the solution: Cell shrinks (______________)! • Hypotonic Solution Osmosis Animations for isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions Hypotonic: The solution has a _____ concentration of solutes and a ______ concentration of water than inside the cell. (Low ______; High _______) Result: Water moves _____ the solution __ ______the cell): Cell _______ and _____ _____ (cytolysis)! • Isotonic Solution Osmosis Animations for isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions Isotonic: The concentration of solutes in the solution is _____ to the concentration of solutes inside the cell. Result: Water moves equally in ____ __________and the cell _____ _______ _____! (Dynamic Equilibrium) What type of solution are these cells in? A _________ B ________ C _________ How Organisms Deal with Osmotic Pressure •Bacteria and plants have ____ _____ that prevent them from over-expanding. In plants the pressure exerted on the cell wall is called ____ _________. •A protist like paramecium has _______ _________that collect water flowing in and pump it out to prevent them from over-expanding. http://www.linkpublishing.com/video-transport.htm#Osmosis_-_Red_Onion •Salt water fish pump salt out of their specialized ___ so they do not dehydrate. •Animal cells are bathed in ______. Kidneys keep the blood _________ by removing excess salt and water. •Active Transport • Cell _____/______ energy • Energy (___) is released in the mitochondria • Actively ______ molecules to where they are needed • Movement from an area of ___ concentration to an area of ____ concentration (materials move __/________ the concentration gradient) • (Low High) • Three Types . . . Types of Active Transport 1. Protein Pumps – ________/_____ proteins that require energy to do work. Each carrier protein is ________. Ie: it can only transport the solute particle that __ into the shape of the carrier protein’s ______ site. Protein changes shape to move molecules: this requires energy! Types of Active Transport Sodium Potassium Pumps (Active Transport using proteins) Protein Pump Examples: a) Calcium Pumps – transport Ca+2 ____ ___ a cell b) Sodium / Potassium Pumps - are important in nerve responses and transport Na+ ___ and K+ ___ a cell http://course1.winona.edu/sberg/ANIMTNS/Na-Kpump.htm Types of Active Transport 2. Endocytosis: taking _____ material ____ a cell • • • • Uses energy Cell membrane in-folds around ____ ________ “cell eating” Forms food ________ & enzymes from lysosomes ________ food Types of Active Transport 2 Types of Endocytosis: i) Phagocytosis – used to absorb _____ particles. ie: ________ “eating” ciliates & ____ ____ ____ “eating” viruses/microbes Types of Active Transport ii) Pinocytosis – used to absorb ______ ________ ie: Intestine cells absorbing fat Types of Active Transport 3. Exocytosis: Forces material ____ ____cell in bulk • Membrane surrounding the material (vacuole formed from golgi apparatus) fuses with cell membrane http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/elearning/raven6/resources06.mhtml • Cell changes ______ – requires energy ie: Hormones or wastes released from cell Endocytosis & Exocytosis animations Types of Active Transport Cytoplasmic Streaming – Cytoplasm _____ _______ around inside the cell - Requires ______ from the cell - Probably uses ____________ of protein in the cytoplasm http://www.youtube.com/wat ch?v=wEK9EdvDz2w