* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Academic Cell Boundary PPT
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
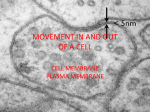
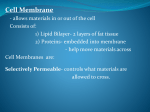
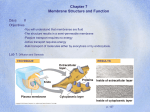
Cell Boundaries/ Cell Membrane Animal cell Plant cell Cell / Plasma Membrane Cell Wall – provides support & protection, usually made of tough fibers 1. The Cell Membrane Complex barrier separating the cell from it's external environment – Holding cytoplasm within cells – Regulating substances entering and exiting cells – Recognizing other cells Is arranged in a double layer called a Lipid Bilayer – Made up of Phospholipids (a phosphate group & 2 fatty acids) 1. The Cell Membrane "Selectively Permeable" membrane that regulates (like a gate) what passes into and out of the cell 1. The Cell Membrane Cell Membranes are FLUID Lipids and Proteins of the Cell Membrane are always in motion 1. The Cell Membrane Membrane Proteins – PROTEIN MOLECULES are EMBEDDED in the Lipid Bilayer – HELP to MOVE Material INTO and OUT of the Cell 1. The Cell Membrane – Often have carbohydrates attached to them to serve as I.D. badges that allow cells to recognize each other 1. The Cell Membrane Diffusion – Movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (no energy required) (put dye in water) Osmosis – Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane 1. The Cell Membrane Facilitated Diffusion / Passive Transport – Uses proteins to move molecules through a cell membrane along the concentration gradient (no energy required) 1. The Cell Membrane Active Transport – Uses proteins to move molecule against the concentration gradient – Requires energy Exocytosis and Endocytosis Exocytosis – process of a cell releasing materials (exiting) Endocytosis – process of cell taking materials in (entering) Exocytosis Example of both: Neurotransmitter • Exocytosis and Endocytosis Example • Neurotransmitter • Osmosis Examples • Hypotonic-Isotonic-Hypertonic (Fold a piece of paper in half) Isotonic – The concentration of solutes is the same inside and outside the cell – Water moves in and out Hypertonic – Solution has a higher solute concentration than the cell – Water moves out Hypotonic – Solution has a lower solute concentration than the cell – Water moves in Draw this on a Youtube http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HqKlLm2MjkI Which cell process will move substances against a concentration gradient? [NC08 EOC] A B C D E diffusion facilitated diffusion osmosis passive transport Requires ENERGY active transport Which diagram represents active transport? [TN09 EOC]