* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Can EVERY molecule pass through the cell membrane freely? Why
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
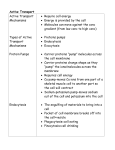
Can EVERY molecule pass through the cell membrane freely? Why or why not? Cell Transport Module Review Sheet Passive Transport Main Idea Passive transport is the movement of molecules across the membrane from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. Materials move across membranes because of concentration differences. It does not require energy input from the cell. Diffusion Osmosis Think of an example of passive transport and list it here Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport occurs when a cell uses energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient. Molecules are moved from lower to higher concentration. It does require energy input from the cell. Endocytosis Cell membrane engulfs a substance and brings it inside the cell “Cell Eating” ENERGY REQUIRED LOW - HIGH Exocytosis The opposite of endocytosis removal of substances out of a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane. Sodium-Potassium Pump Movement of Na+ and K+ ions across a membrane through the use of a pump. Requires Energy in the form of ATP & a Carrier Protein Understanding Check Write the type of transport then indicate if energy is required or not required.