* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download dna methylation
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetic clock wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA methylation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
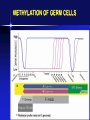
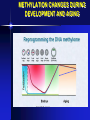
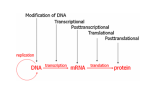
The Pathogenesis of Diseases from Genetic and Genomic Point of View - 4 THE DEFLATION OF GENOMIC BUBBLE AND THE HOPES OF EPIGENETICS PROBLEMS • Small genetics and big genomics (and strong commercial influence) • Genome sequencing is already routine (cca 1000 eur) • State and consumer eugenics? • Is there an improvement in our knowledge about health and disease 15 years after the human genome project? (yes, but…) • Is it possible to apply in everyday medicine? (Yes in oncology) Rose H, Rose S: Genes, Cells and Brains. Verso UK & USA 2013 WHERE THE THINGS WENT WRONG? • • • • Small genetics and big genomics (and strong commercial infulence) Genome reading is already routine (cca 100 eur) State and consumer eugenics? Is there an improvement in our knowledge about health and disease 15 years after the human genome project? • Is it possible to apply in everyday medicine? DNA IS A “DEAD” MOLECULE WORKING ONLY IN ITS VERY COMPLEX ENVIRONMENT (CHROMOSOMES, CELLS…) C.H. WADDINGTON. CCA 1950 EPIGENETICS AND LONG AGO LAMARCK (THE LONG NECK OF GIRAFFE) THE SECRETS OF CELL/TISSUE DIFFERENTIATION The term ‘epigenetic’ refers to all heritable changes in gene expression and chromatin organization that are independent of the DNA sequence itself EPIGENETICS Histone modifications DNA methylation microRNAs Goldberg AD et al Cell. 2007 Feb 23;128(4):635-8. Identical twins, different hair colour THE BASIC EPIGENETIC PROCESSES METHYLATION OF DNA (GENE BLOCK) HISTONE ACETYLATION (ACTIVATION) RNA MODIFICATIONS (ALTERNATIVE SPLICING) TRANSLATION CONTROLL (siRNA) SOMATIC = DIFFERENTIATION AND OTHER CHANGES IN CELL FUNCTION TRANSGENERATIONAL! INTERACTION WITH THE ENVIRONMENT DNA CYTOSINE METHYLATION ALSO ON THE OTHER CHAIN (CG – GC) MITOSIS – YES? NO? COMPLICATED ENZYME SYSTEMS (CODED IN DNA!) METHYLATION OF GERM CELLS Diapo 11 METHYLATION CHANGES DURING DEVELOPMENT AND AGING AND BACK ??? DNA METHYLATION • DNA methylations consist of adding –CH3 groups to cytosines in CpG islands • Methylations regulate gene expression (block) and maintain the stability of genome • • • • Gene expression in general Imprinting Silencing of repetitive sequences, pseudogenes... Inactivation of the 2nd X chromosome • AGING, CARCINOGENESIS.... • TRANSGENERATIONAL METHYLATION !!! Hongerwinter 1944 • • • • German’s blocked food to the Dutch in the winter of 1944. Calorie consumption dropped from 2,000 to 500 per day for 4.5 million. Children born or raised in this time were small, short in stature and had many diseases including, edema, anemia, diabetes and depression. The Dutch Famine Birth Cohort study showed that women living during this time had children 20-30 years later with the same problems despite being conceived and born during a normal dietary state. HISTONE MODIFICATIONS • Coating and packing of DNA? Yes, but… • Covalent modifications: acetylation, methylation, phosphorylations, etc. • Common: acetylation and methylation of amino terminal lysins H3 and H4 histones • These modifications are essential for the regulation of transcription, replication and also DNA maintenance • They are coordinated with DNA methylation • Catch 22: The histone structure and everything around them is coded in DNA EXTREMELY COMPLICATED BASIC PRINCIPLE: WRITER – makes modifications READER – reads the signs and gives instructions what to do in the cell ERASER All “nonheritable” diseases have (epi)genetic background Most “heritable” diseases are influenced by the environment Food Infections Trauma Toxins Life style Psychical Social ……… EPIGENETICS?? • Frustrations from the results of modern genomics and other „omics“ from the point of view of everyday practical medicine • Interpretation of the results from microchips and genome reading? • Too many genes (and their polymorphisms) for common diseases • The missing part of heritability – the genome is cooperating very intensively with the environment! • This cooperation is possible through „epigenetic“ processes