* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene expression An organism`s genome is the complete set of
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
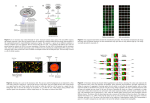
Gene expression An organism’s genome is the complete set of genes in each of its cells. Given an organism, every one of its cells has a copy of the exact same genome, but ◆ not all its cells express the same genes ◆ different genes express under different conditions Measure the levels of the various mRNAs in a cell in a specific state ⇒ gene expression 1 profile of cell in that state ⇒ cell state. DNA microarrays One of the most promising tools for obtaining gene expression data is the DNA microarray. A DNA microarray is a tiny glass slide on which genes (purified single-stranded cDNA sequences in solution) have been robotically printed in an (approximately) rectangular array; each spot on the array corresponds to a single gene. 2 Experimental procedure ◆ Prepare DNA microarray. ◆ Prepare labeled test sample. cellular contents → mRNA (isolate & purify) → cDNA (reverse transcription) → (add flourescent dye) sample 3 Experimental procedure (continued) ◆ Flood the microarray with the labeled sample. ◆ Whenever there is cDNA in the array complementary to mRNA in the sample, the two will hybridize. ◆ Hybridization is allowed to take place, then the array is washed and dried. ◆ The array is scanned with a laser microscope. 4 Scanned image 5 Interpreting the scanned image ◆ High intensity spot ⇒ the DNA at that spot corresponds to some RNA in sample. ◆ Low intensity spot ⇒ no RNA in sample that corresponds to the DNA at that spot. ◆ Intensity ~ RNA abundance. ◆ For any gene, can compare intensities across different samples (but shouldn’t compare intensities for different genes for the same sample). 6 Comparing two scanned images Control Treatment 7 8 Paradigm [expressed] gene ➡ mRNA amount of mRNA in cell ➡ transcription level of gene change in state of cell → change in gene expression pattern within cell → change in mRNA abundance in cell → change in spot intensity pattern 9 Uses of DNA microarrays DNA microarrays can be used to compare gene expression patterns, multiple genes at a time: ◆ Which genes are expressed in which cells and under what conditions. ◆ Which genes are expressed differently in diseased cells compared to normal cells. ◆ Which genes are expressed differently when a patient is administered a drug. 10 Raw array speckles (B) (A) Light Background (C) Shape 11 Technology differences ◆ Pin spotting or inkjet printing or photolithography ◆ 1-sample or multi-sample ◆ Almost-complete sequences (cDNA) or subsequences (oligoneucleotides) 12 Processing steps Spotted Image 4000 2000 Probability Interv 6000 8000 Statistical Analysis 0 Raw Image 0 100 200 300 Genes 13