* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nitty Gritty Cell Parts
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
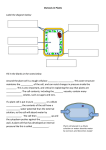
NITTY GRITTY CELL PARTS CELL THEORY •All living organisms are composed of cells. They may be unicellular or multicellular. •The cell is the basic unit of life. •Cells arise from pre-existing cells. PROKARYOTE VS. EUKARYOTE ANIMAL CELL ANIMAL CELL • Nucleus - the command center of the cell. This houses nearly all the genetic material of the cell. • Nucleolus - makes RNA and ribosomes • Rough ER - transports proteins that were made on the attached ribosomes • Smooth ER - involved in lipid (fat) production. • Ribosomes - the factories of the cell. Site of protein synthesis. • Golgi Apparatus/Body - the post office of the cell. The Golgi receives proteins from the ER. The packaged proteins are either sent to other parts of the cell, or sent to the cell membrane for secretion. • Lysosomes - the cell's recycling plants. Their role is to break down materials. ANIMAL CELL • Cell Membrane - the border guard of the cell - this envelope surrounds the cell and controls which substances can move in and out of the cell. • Mitochondria - the power station of the cell. Make ATP. ATP is the energy currency of the cell, used in almost all energy-requiring cellular processes. • Small Vacuoles – small storage/transport PLANT CELL PLANT CELL • Chloroplasts - Makes Sugar from Sunlight • Cell Wall - the defensive walls of the plant. • Vacuole - The large vacuole is filled with water and various solutes. PLANTS VS. ZOMBIES ANIMALS OSMOSIS • Movement of Water across a semipermeable membrane. DIFFUSION • Movement of a solute across a membrane. • *Solutes are anything other than water. TYPES OF DIFFUSION • Passive – Doesn’t need energy • Can pass through membrane no help • Facilitated Diffusion – No energy but needs protein channel. • Active – Needs Energy HYPO, HYPER, ISOTONIC • Hypotonic – Cell more solutes; solution less solutes • Isotonic – Equal • Hypertonic – Cell less solutes; solution more solutes CELL MEMBRANE LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION