* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 15: Protein Synthesis
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
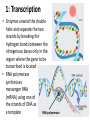
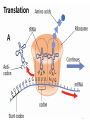
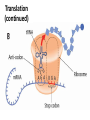
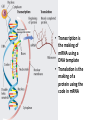
Chapter 15: Protein Synthesis Leaving Certificate Biology Higher Level Protein Synthesis: DNA versus RNA • DNA: – Double-stranded – Deoxyribose – Nucleotides: • Adenine • Thymine • Guanine • Cytosine • RNA: – Single-stranded – Ribose – Nucleotides: • Adenine • Uracil • Guanine • Cytosine • Protein synthesis is carried out in three distinct stages: transcription; translation; and protein folding 1: Transcription • Enzymes unwind the double helix and separate the two strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases only in the region where the gene to be transcribed is located • RNA polymerase synthesises messenger RNA (mRNA) using one of the strands of DNA as RNA polymerase a template 2: Translation • mRNA moves to cytoplasm and combines with a ribosome made up of two ribosomal RNA (rRNA) subunits • Each 3-base (triplet) sequence of the mRNA is a codon that specifies either a start codon, a particular amino acid, or a stop codon • Transfer RNA (tRNA) is another type of RNA – it is found free-floating in the cytoplasm and is responsible for carrying one amino acid – Remember amino acids are the building blocks of proteins • tRNA has a 3-base (triplet) sequence called the anticodon that is complementary to a particular codon on the mRNA Step 3: Translation (cont.) • Each tRNA in turn (with its own amino acid) lines up with the mRNA in the ribosome and an amino acids are joined together in a long polypeptide line which will form the protein • This process continues until the stop codon on the mRNA is reached at which point all the translation machinery separates and the protein is released and it folds up into its active form and goes and carries out its specific function Translation Translation (continued) • Transcription is the making of mRNA using a DNA template • Translation is the making of a protein using the code in mRNA