* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Migraine Visual Aura
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Convolutional neural network wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
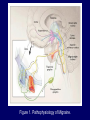
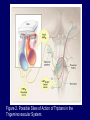
932-5 Migraine Visual Aura Pathophysiology The pain of migraine headache is thought to have a neurogenic basis. Migraine involves dysfunction of brain-stem pathways that normally modulate sensory input. The key pathways for the pain are the trigeminovascular input from the meningeal vessels, which passes through the trigeminal ganglion and synapses on second order neurons in the trigeminocervical complex. Figure 1. Pathophysiology of Migraine. Pathophysiology These neurons, in turn, project through the quintothalamic tract, and after decussating in the brainstem, form synapses with neurons in the thalamus. Pathophysiology There is a reflex connection between neurons in the pons in the superior salivatory nucleus, which results in a cranial parasympathetic outflow that is mediated through the pterygopalatine, otic, and carotid ganglia. Pathophysiology This trigeminal–autonomic reflex is present in normal persons and is expressed most strongly in patients with trigeminal–autonomic cephalgias, such as cluster headache and paroxysmal hemicrania. Pathophysiology Brain imaging studies suggest that important modulation of the trigeminovascular nociceptive input comes from the dorsal raphe nucleus, locus ceruleus, and nucleus raphe magnus. Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB, Ferrari MD. Migraine – Current understanding and treatment. N Engl J Med Jan 1, 2002; 346 (4):257-270. Figure 2. Possible Sites of Action of Triptans in the Trigeminovascular System. Acknowledgement Figures 1, 2 published Courtesy of PJ Goadsby, M.D DSc Goadsby PJ, Lipton RB, Ferrari MD. Migraine – Current understanding and treatment. N Engl J Med 2002, 346 (4): 257-270. http://library.med.utah.edu/NOVEL/Wray/