* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life of a Protein #1 This outline describes the job of a specialized
Survey
Document related concepts
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
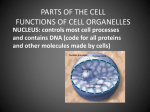
Life of a Protein #1 This outline describes the job of a specialized cell in the human body. Determine 1) the cells location in the human body and 2) its job description from these clues. The NUCLEUS gets a signal. Genes in the NUCLEUS that code for specialized proteins are activated. Messanger RNA is produced in the NUCLEUS. mRNA travels to the cytoplasm through NUCLEAR PORES. RIBOSOMES are produced by the NUCLEOLUS. RIBOSOMES move to and attach to the ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER). RIBOSOMES on the ROUGH-ER binds to the mRNA and translates the code in the mRNA sequence into a chain of amino acids (the primary structure of the proteins). Finished amino acid strands are transferred to the lumen of the ROUGH-ER. Amino acid chains are modified and folded inside the ROUGH ER into secondary and tertiary structures. The proteins are transported via VESICLES to the GOLGI APPARATUS. At the GOLGI APPARATUS, the proteins are further modified with the addition of carbohydrates. The proteins are loaded into GOLGI SECRETORY VESICLES. These GOLGI SECRETORY VESICLES also synthesize lactose. These VESICLES are impermeable to lactose, so the lactose stays inside the VESICLE. The VESICLES are full of stuff (high concentration of proteins and lactose). Water rushes into the VESICLES due to osmosis (we will cover osmosis in this lecture). GOLGI SECRETORY VESICLES swell with water, proteins, and lactose. The GOLGI SECRETORY VESICLES move to the PLASMA MEMBRANE. The water, proteins, and lactose exit the CELL via EXOCYTOSIS into a duct. Milk duct Cells location:___________________ Produce protein for breast milk Cells job:_______________________ Casein protein Protein:________________________ Life of a Protein #2 This outline describes the job of a specialized cell in the human body. Determine 1) the cells location in the human body and 2) its job description from these clues. Epithelial cells release proteins, which communicate to our cell through the PLASMA MEMBRANE. The NUCLEUS gets the signal. Genes in the NUCLEUS that code for specialized proteins are activated. Messanger RNA is produced in the NUCLEUS. mRNA travels to the cytoplasm through NUCLEAR PORES. RIBOSOMES are produced by the NUCLEOLUS. RIBOSOMES move to and attach to the ROUGH ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER). RIBOSOMES on the ROUGH-ER binds to the mRNA and translates the code in the mRNA sequence into a chain of amino acids, the primary structure of the proteins. Finished amino acid strands are transferred to the lumen of the ROUGH-ER. Amino acid chains are modified and folded inside the ROUGH ER into secondary and tertiary structures. The proteins are transported via VESICLES to the GOLGI APPARATUS. At the GOLGI APPARATUS, the proteins are packaged in the GOLGI SECRETORY VESICLES. The GOLGI SECRETORY VESICLES move to the PLASMA MEMBRANE. The proteins exit the CELL via EXOCYTOSIS, but stay attached to the outside of the PLASMA MEMBRANE. The proteins sticking out from the CELL MEMBRANE and attach to proteins sticking out from the epithelial cells. Blood vessel Cells location:___________________ Produce protein to stop cell movement Cells job:_______________________ White blood cell Type of cell:____________________