* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9 homework due 3/31/08 1a. Will lacZ be transcribed and
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transcription factor wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
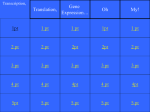
Chapter 9 homework due 3/31/08 1a. Will lacZ be transcribed and translated if E. coli are grown in media with only lactose as a sugar source? YES What factors will be bound to the lacO and lacP sites these conditions and why? AT P, the CRP-cAMP COMPLEX WILL BE BOUND + RNA POLYMERASE. NOTHING WILL BE BOUND TO O. b. Will lacZ be transcribed and translated if E. coli are grown in media with only glucose as a sugar source? NO What factors will be bound to the lacO and lacP sites these conditions? Repressor will be bound at O. c. Will lacZ be transcribed and translated if E. coli are grown in media with both lactose and glucose as sugar sources? NO What factors will be bound to the lacO and lacP sites these conditions and why? Nothing will be bound. cAMP levels will be low, so CRP-cAMP complex will not form or bind to P and neither will RNA Pol. Repressor will be inactivated by binding to lactose so it will not be bound to O. d. Will lacZ be transcribed and translated if E. coli are grown in media with only glycerol as a sugar source? NO What factors will be bound to the lacO and lacP sites these conditions? Repressor will be bound to O. CRP-cAMP will be bound to P, but because repressor is bound to O, RNA Pol won’t have access to the promoter. 2a. Will the trp structural genes be transcribed and translated when E. coli are grown in media supplemented with high amounts of the amino acid tryptophan? NO What factors will be bound to the trpO and trpP sites? Tryptophan (the thing the trp operon enzymes make) will bind to aporepressor to make active repressor, which will bind to O and prevent RNA Pol from binding to P. b. Will the trp structural genes be transcribed and translated when E. coli is grown in low to moderate concentrations of tryptophan? The levels of trp will not be high enough to turn all aporepressor into active repressor so some transcripts will begin. There will not be enough active repressor to ensure that repressor is bound to operator at all times. Therefore transcription will begin. However, transcription will be attenuated, so the structural genes will not be translated. Explain…. Under low to moderate trp concentrations, there will be sufficient charged trp-tRNAs that the ribosome does need to pause when it gets to the place in the leader where it should insert two adjacent trps. Thus, the 3-4 stem loop region Chapter 9 homework due 3/31/08 will fold into an attenuator structure and the RNA Pol will fall off the DNA… The mRNA will be attenuated. 3. Will the trp structural genes be transcribed and translated if mutations prevent the 3-4 stem loop in the trpA region from forming? Yes, provided there is not so much trp around to activate the aporepressor. 4. Why is attenuation a good strategy of gene control for operons that encode the enzymes that synthesize amino acids? Because the exact concentration of the end product regulates the level of mRNA synthesis, the levels of product can be finely regulated by the conditions. Whenever aa concentrations rise a bit, the relative amount of transcripts that reach full length drop; but whenever the aa levels drop, full length transcription goes right back up. 5a. What are the similarities and differences between positive and negative control of transcriptional regulation? Positive control means that the default mode of a gene is OFF unless it gets the help of a transcriptional activator. Negative control means that the default mode of a gene is ON unless a repressor protein comes along and actively prevents RNA Pol from binding. In both cases something binds to promoter region’s DNA to regulate transcription—either positively or negatively. b. What are the similarities and differences between inducible and repressible forms of negative control? These are the same in that the gene is on unless a repressor protein binds and turns the operon off. Also, at least in the cases we studied (lac and trp) the repressor proteins are made constitutively. They differ in that for the lac operon the repressor alone is sufficient to bind to DNA and block transcription. The operon is induced when lactose (the inducer) binds to the repressor and prevents it from binding to operator, lacO. In contrast, the trp aporepressor is inactive until it binds to tryptophan (the corepressor); the tryptophan-repressor complex binds DNA (at trpO) and blocks transcription. 6. Why are operons that make enzymes involved in biosynthetic pathways regulated one way, while operons that make enzymes involved in degradative pathways regulated differently? The genes in biosynthetic pathways need to be on when they need to make product. But. when the end product levels are sufficient to meet the needs of the cell, there is no need for more synthesis of the product, so the operons slow down or cease transcription. They are repressible by the end product. In contrast, the genes that make enzymes that catabolize sugars, only need to be active when the sugar is present in the environment. It would waste energy (and Chapter 9 homework due 3/31/08 lower survival chances) to make the proteins when they aren’t necessary. Thus, these genes are in the off mode until the sugar (or some derivative of the sugar) is present to induce (or derepress) them. 6. E. coli have various mutations in their lac operons (shown in left hand column). Will the LacZ genes be expressed if the “bugs” are grown in the various conditions listed across the top of the table? Refer to table 11.2 (p. 453) to see how these different sugars effect cAMP concentrations. Lac expression is completely dependent on positive control, so if glucose is around the lac operon will be inactive. LacZ gene cannot ever be expressed if the Promoter (P) is mutant because RNA polymerase won’t be able to bind to DNA. It also won’t be expressed if lacZ gene itself is mutant. Is binds to O and will not come off in the presence of lactose. Oc is a mutation in the binding site for repressor. It will affect only the lacZ genes downstream of it on same DNA. Genotype of lac operon I+P+O+Z+ I+P-O+Z+ I+P+OcZ+ I+P+O+ZIsP+OcZ+ ISP+O+Z+ Lactose only yes no yes no Yes no Sugar source Glucose only Glucose + lactose no no no no no no no no no no no no glycerol no no yes no yes no 7. Are the partial diploids listed below inducible with lactose, constitutively expressed or uninducible? Assume there is no glucose around… O+Z+/OcZ+_____constitutive Is/I+_______ never expressed OcZ-/O+Z+____inducible____ ISOcZ+/I-O+Z-+____constitutive_____ OcZ+/O+Z+____constitutive____ I-OcZ-/I+O+Z+_______constitutive___ 8.Define the terms listed at the end of each chapter covered.