* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download slides - István Albert
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Whole genome sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Human Genome Project wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Inversion Probe wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
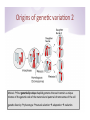
2014 -‐ BMMB 852D: Applied Bioinforma9cs Week 9, Lecture 18 István Albert Biochemistry and Molecular Biology and Bioinforma9cs Consul9ng Center Penn State “Holis0c” Data Analysis • Put together EVERY STEP of the analysis BEFORE op9mizing any of the intermediate steps • Try to imagine what the end result needs to look like and work towards that goal • Think of an ar9st drawing portrait à it is a successive refinement of the en9re image Origins of gene9c varia9on 1 • A regular diploid human cell contains 46 chromosomes • 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes = 46 (22 pairs + sex chromosomes XX(female) XY(male) • One set of chromosomes inherited from each parent Note that the reference genome is a “consensus” across all chromosomes of DNA pooled from mul9ple individuals Origins of gene9c varia9on 2 Meiosis à four gene0cally unique haploid gametes that each contain a unique mixture of the gene9c code of the maternal and paternal chromosomes of the cell gene9c diversity à phenotype à natural selec9on à adapta9on à evolu9on Origins of human gene9c varia9on 3 • No two humans are gene9cally iden9cal (not even monozygous twins that start out as such) • About 30 new varia9ons per genera9on. • An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a gene9c locus • Both alleles are the same à homozygotes. • If the alleles are different àheterozygotes. Single nucleo0de polymorphisms: SNP • A single nucleo9de — A, T, C or G — in the genome differs between members of a popula9on or chromosome pairs • Originally defined as occurring at least in 1% of the popula9on (these defini9ons may shic in 9me) à SNV (single nucleo9de variant) if observed very rarely • SNP, SNV à may fall within coding sequences of genes, non-‐coding regions of genes, or in the intergenic regions • DIP: dele9on/inser9on polymorphism, • Single Nucleo0de Polymorphism Database[1] (dbSNP) • As of 26 June 2012, dbSNP listed 187,852,828 SNPs in humans. SNP Calling • Not nearly as well standardized as one might think In 2006 the Archon Genomics X PRIZE was to award $10 million to the first team to rapidly, accurately and economically sequence 100 whole human genomes to a level of accuracy never before achieved. First X-‐Prize challenge (cancelled) Blog: Blue Collar Bioinforma0cs 8% of GATK and 14% of samtools SNP calls are discordant! SNP calling checklist • Unique sample or pooled samples? – unique samples à the expecta9on for each allele will be 50% • External informa9on à SNPs tend to occur in clusters • Coverage and quality filtering are very important A large number of SNP callers have been published • Each is good at some aspects (well publicized) – and not so good at others (less publicized) • SNP calling seems deceivingly simple – why can’t we just enumerate all the bases at a posi9on? • Greatest challenge: misalignments à incorrect SNP calls 10,000 exonic sites where the RNA does not match the DNA RNA-‐DNA difference (RDD) All 12 possible categories of discordance have been observed A few statements from the paper 1 year later Claim: at least 90% of the sites in the paper are false posi0ves Genomes Unzipped Blog Let’s compare aligners: bwa vs bow9e2 Homework 18 1. Install bow9e2 2. Create alignments with bow9e2 and bwa. 3. Compare their outputs in IGV and look for similari9es and dissimilari9es in the alignments at the simulated error rate of 10% Extra credit (10 points): Are there parameter seungs for bow9e2 that would make it more compe99ve with bwa when mapping reads with high error rates?