* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
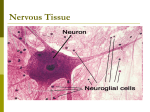
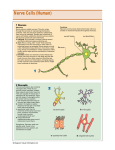
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System The Nervous System is the major controlling and communicating system in the body The Nervous System The means of communication is Electrical impulses Which causes immediate responses 3 major Functions of the Nervous System Monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body These changes are called stimuli and the gathered info is called sensory input 3 major Functions of the Nervous System Process and interpret sensory input and make decisions about what should be done. This is called integration 3 major Functions of the Nervous System Effect a response by activating muscles or glands. The response is called motor output 3 major Functions of the Nervous System So…… sensory input integration motor output Works along with the endocrine system The Nervous System 2 Classifications: CNS Central Nervous System Made of brain and spinal cord The Nervous System 2 Classifications: PNS Peripheral Nervous System Made of nerves (spinal and cranial) Nerve Tissue 2 kinds: 1. Supporting Cells Nerve Tissue 2 kinds: 2. Neurons Nerve Tissue Neuroglia Supporting cells in the CNS Support, insulate, and protect neurons Not able to transmit impulses Never lose ability to divide so most brain tumors are gliomas. Tumors are formed by neuroglia Nerve Tissue Neuroglia 1. Astrocytes Star shaped Cling to neurons Form a barrier btw neurons and capillaries Protect neurons from harmful substances in the blood Pick up excess ions and neurotransmitters Nerve Tissue Neuroglia 2. Microglia Phagocytes that dispose of dead brain cells and bacteria Nerve Tissue Neuroglia 3. Oligodendrocytes Produce insulating covering called myelin sheath Nerve Tissue Supporting cells in the PNS • Schwann cells Form the myelin sheath around nerve fibers in the PNS Nerve Tissue Supporting cells in the PNS 2. Satellite cells Protective, cushioning cells NEURONS Nerve Cells Transmit nerve impulses (messages) Made of: Cell body Axon Dendrite NEURONS Nerve Cells Cell body Center of cell. Contains the nucleus Process or fibers extend from the cell body NEURONS Nerve Cells Axon conducts impulse away from the cell body Only one per neuron NEURONS Nerve Cells Dendrite conducts impulse toward the cell body 100s per neuron 1. dendrites 2. nucleus 3. Cell body 4. Myelin 5. axon sheath NEURONS Nerve Cells Synapse junction between 2 neurons. The 2 neurons never actually touch NEURONS Nerve Cells Myelin white fatty covering on the axon. They protect and insulate Also increase the rate of nerve impulse transmission NEURONS Nerve Cells Myelin if the myelin sheath is destroyed as in multiple sclerosis, the person loses the ability to control their muscles. NEURONS Nerve Cells Myelin of the CNS White matter myelinated fibers Gray matter unmyelinated fibers NEURONS Classification Functional classification groups are according to the direction the nerve impulse is traveling Afferent or Efferent NEURONS Classification Afferent Sensory. Carries impulse from organs to CNS Efferent Motor. Carries impulse from CNS to muscles, glands. Properties of Nerve Impulses Irritability Ability to respond to a stimuli Conductivity Ability to transmit impulses to other neurons, muscles, glands Properties of Nerve Impulses Electro-chemical event. Na ion enters cell K ion leaves the cell causing a resting state. NA K pump depolarization repolarization Properties of Nerve Impulses Neurons release neurotransmitters to influence other neurons. This opens a specific ion channel Neurotransmitter? acetycholine NA K pump Active transport Reflex A reflex is a rapid predictable response to a stimulus Autonomic Somatic Regulates activities of smooth muscles, the heart and glands. Stimulates skeletal muscles Reflex Autonomic Salivary reflex Pupillary reflex Somatic Patellar reflex Sucking reflex Reflex Normal reflexes indicate normal nervous system functions Plantar reflex (Babinski) The normal reflex is toe flexion. If the toes extend and separate, this is an abnormal finding called a positive Babinski's sign. Central Nervous System CNS Neural Tube How nervous system 1st appears in embryo Ventricles Chambers. We have 4 Neural Tube Deficiency of Folic acid = neural tube birth defects Folic Acid Also called B9 Leafy vegetables such as spinach and turnip greens dried beans and peas, fortified cereal products,sunflower seeds and certain other fruits and vegatables are rich sources of folate. Some breakfast cereals are fortified with 25% to 100% of the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for folic acid.