* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Medial Longitudinal Fissure
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Emotion and memory wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Sensory cue wikipedia , lookup
Emotion perception wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Executive functions wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Motor cortex wikipedia , lookup
Superior colliculus wikipedia , lookup
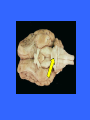
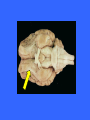
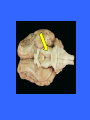
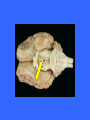
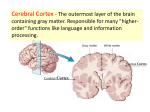
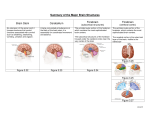
Dorsal Ventral Mid-Sagittal Coronal Horizontal 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Cerebellum Muscle Tone, Balance, and Finely Coordinated Movement Occipital Lobe Area V1 Primary Motor Cortex Medial Longitudinal Fissure Divides the brain into two equal hemispheres. What are the basic functions of each of the four cerebral lobes? Frontal – Cognition, Planning, Motor Control Parietal – Somatosensory input, Proprioception, Language Temporal – Memory, Emotion, Audition, Sexual & Social Behaviour Occipital - Vision Pons Connect the Medulla to the Midbrain and Thalamus. Contains numerous tracts including the Cortico-spinal tracts and Reticular Formation Olfactory Tract Relay olfactory impulses from the olfactory bulbs to the entorhinal cortex Cerebral Peduncles Contain descending fibres of the Corticospinal Tracts Receives afferents from sensory modalities and relay via Thalamus Mammillary Bodies Sexual Arousal Memory Emotion Trapezoid Bodies Sound localization via interneurons that inhibit ipsilateral signals and amplify contralateral signals to increase amplitude and temporal differences Corpus Callosum Relay signals between the two hemispheres Pineal Body Endocrine functions: secretes melatonin, controls daily rhythms In vertebrates other than humans: secretes hormones affecting reproductive behaviour Inferior Colliculus Intermediate nucleus for processing auditory signals before they are transmitted to the primary auditory cortex Cingulate Gyrus Pain perception, Visceral Responses to Emotion, and Planning of Motor Action Anterior Commisure Globus Pallidus Posture, Muscle tone, and control of Eating and Drinking Column of the Fornix Memory and Control of Eating Hippocampus Emotion, motivation, navigation by cognitive maps, learning, and the consolidation of long-term memory Head of the Caudate Nucleus Inhibitory Control of Movement Periaqueductal Gray Contains opiate neuroreceptors and neurons that release endorphins Implicated in the sensation and suppression of pain Implicated in the control of aggression and in female sexual behaviour. Internal Capsules Nerve fibres running from the thalamus to the left or right cerebral cortex and from the cerebral cortex to the thalamus, brainstem, and spinal cord Superior Colliculus Processes spatial aspects of visual info Directs eye movement in the direction of visual attention Optic Tract Relays amalgamated visual information from the Optic Chiasm to the LGN Putamen Posture and Movement Control Claustrum Anterior: Cortical Pain Centre Posterior: Language