* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biological synaptic functioning ordering activity
Dendritic spine wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Vesicular monoamine transporter wikipedia , lookup
Long-term depression wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic noise wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
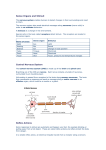
The Biological approach to Psychology Synaptic functioning Put these processes in the correct order Activity in the receptors causes a change in the second neurone which increase or decreases the likelihood of an action potential in the second neurone Electrical impulses pass down the axon of the first neurone Neurotransmitter molecules are recycled into the pre-synaptic neurone. Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse and attach to receptors on the post synaptic membrane Vesicles fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane and release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft Vesicles that contain neurotransmitters move towards the pre-synaptic membrane. NGfL Cymru Answer Electrical impulses pass down the axon of the first neurone Vesicles containing neurotransmitters move towards the presynaptic membrane. Vesicles fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane and release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft Neurotransmitters diffuse across the synapse and attach to receptors on the post synaptic membrane Activity in the receptors causes a change in the second neurone which increase or decreases the likelihood of an action potential in the second neurone Neurotransmitter molecules are recycled into the pre-synaptic neurone. Based on page 4 and 5 of Psychology for WJEC AS level by Russell and Jarvis NGfL Cymru