* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam Review 4B - Iowa State University
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Long non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
RNA interference wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
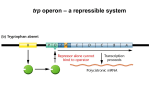
BIO 313 Exam Review 4B Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Laura Bio 313 Dr. Rodermel 11/15/15 Complete the following table: Lac Operon Mutation Lactose Present Beta-Gal Permease Lactose Absent Beta-Gal Permease lacI+ lacP+ lacO+ lacZ- lacY+ lacI- lacP+ lacO+ lacZ+ lacYlacI+ lacP- lacOc lacZ+ lacY+ lacI+ lacP+ lacOc lacZ- lacY+ lacI- lacP+ lacO+ lacZ- lacY- / lacI+ lacP- lacO+ lacZ+ lacY+ lacI+ lacP- lacO+ lacZ+ lacY- / lacI+ lacP+ lacOc lacZ- lacY+ 1. Match the definition to corresponding term below: miRNAs Enzyme that cleaves hairpins from dsRNA and gives rise to small miRNAs (22 nucleotides long) Primary miRNA transcript A large multisubunit, ribonucleoprotein complex that builds miRNA Dicer Come from dsRNA (ex. ds RNA viruses, some mRNAs that can form hairpins) RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) Arise from specific genes (~450 different genes in humans) siRNAs Has long inverted repeats that form hairpins 2. Which of the following are responsible for forming the sex pili? a. Conjugation b. Enhancers c. Fertility Factor d. Kineticore and Microtubules 1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center 515-294-6624 [email protected] http://www.si.iastate.edu 3. In a partial diploid cell the second copy of the lac operon is found on the a. Bacterial chromosome b. F factor c. Regulator Region d. Plasmid 4. Which of the following components of the lac operon forms a trans-acting product a. LacA b. LacI c. LacP d. LacO 5. All of the following are structural genes except a. LacZ b. LacA c. LacO d. LacY 6. If lacO is mutated to lacOc, what is the result a. The structural genes are not expressed b. The RNA polymerase is unable to bind c. The repressor binds the operator d. The structural genes are always expressed 7. Which of the following is the correct relationship between glucose and catabolite repression a. High glucose, high levels of cAMP b. High glucose, high levels of CAP c. Low glucose, low levels of cAMP d. Low glucose, high levels of cAMP 8. When the cAMP-CAP complex is bound which of the following takes place? a. Polymerase binds the lacP more efficiently b. Polymerase if unable to bind to the lacP c. The repressor is unable to bind the operator d. The lacP is mutated 9. All of the following are differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic gene regulation a. Eukaryotes have mRNA processing b. Eukaryotes use histones and chromatin remodeling c. Eukaryotes have non-coupled tx and tl d. Eukaryotes have operons 10. Histone modification result from a. A neutralization of negative charges from DNA b. A neutralization of positive charges from DNA c. A neutralization of negative charges from histones d. A neutralization of positive charges from histones 11. Which of the following closes chromatin confirmation? a. Acetylation b. Deacetylation c. Tx Activation d. Non-methylated DNA 12. How do eukaryotes coordinate gene expression? a. Operons b. Enhancers c. Response Elements d. Regulator Proteins 13. Which of the following is located furthest upstream? a. Enhancers b. Core Promoter c. Regulatory Promoter d. Structural Genes 14. Which of the following is not a way that repressors act? a. Compete with activators b. Bind to the activator c. Bind the silencer d. Allow for assembly of basal tx apparatus 15. Which of the following is the function of an insulator? a. Blocks all enhancers b. Allows tx of all genes c. Allows for specificity of gene expression d. Blocks the effects of all promoters 16. Where are AU-rich elements located and what is its effect? a. 5’ UTR, rapid degradation b. 5’ UTR, slow degradation c. 3’ UTR, rapid degradation d. 3’ UTR, slow degradation 17. RNAi likely evolved from a. DNA plasmid b. DNA virus c. RNA virus d. Protein products 18. This phase consists of growth and protein production to allow for cell division a. M Phase b. G2 Phase c. S Phase d. G1 Phase 19. The attachment point for spindle microtubules is the a. Telomere b. Centromere c. Origin of Replication d. Homologous Pair 20. Draw out how miRNA and siRNAs function to inhibit translation? miRNAs 21. Which phase of mitosis is depicted below? e. f. g. h. Anaphase Telophase Metaphase Prophase 22. Fill out the following table: siRNAs 23. A parent cell is 2n with a haploid number of 4, draw this cell from Prophase I to the four gametes that will be formed 24. Two parents are AA x aa, cross these individuals through to an F2 generation (include phenotypic ratios) 25. List the three postulates for Mendel’s law of segregation a. b. c. 26. The allele G (gray) is dominant to allele g (white) in rabbit coat color. What would the resulting genotypic and phenotypic ratios be if a Gg was crossed with a white rabbit? 27. Define the two rules: a. Addition b. Multiplication





![[001-072] pierce student man](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017104672_1-497120343b128453965f3c5043e36ba3-150x150.png)