* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHEMISTRY
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
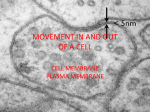
AP Biology Study Guide for Ch. 6 (Tour of the Cell) & Ch. 7 (Membrane Structure and Function): September 2013 We are finally finished with the oh-so-exciting world of chemistry (and biochemistry and organic chemistry). Hooray! Now we finally get to study living things, starting with the basic unit of life: CELLS. Chapter 6 takes you through the structures and functions of all the parts of cells. You need to memorize the names, structures, and functions of ALL of these parts! Chapter 7 focuses in on the cell membrane and goes into more detail about how this part of the cell functions to control what enters and leaves a cell (= “selective permeability”). The good news is that if you were paying attention in Biology I, this should all be review! I. SCHEDULE 2013 for Chapters 6 & 7 Monday (9/30) Tues *Go over Ch. 6 & 7 *Work on Cell Study Guide Sketching Project *Assign Cell Sketching Project Wed *Reading Quiz Ch. 6 *Lecture Ch. 7 Fri *Go over Reading Quiz *Lecture Ch. 7 *Assign Pre-lab #4Diffusion and Osmosis Fri *Finish Inv. 4-Diffusion & Osmosis—Assign Write-up (Due Fri 10/18) *Lecture Ch. 7 *Assign FRQ Fri Monday (10/7) *Lecture Ch. 7 Tues *Investigation 4Diffusion & Osmosis (Pre-lab DUE!) Wed *Investigation 4Diffusion & Osmosis Mon (10/14) *Finish Ch. 7 Tues *TEST Chapters 6 & 7 *PACKET DUE, *Flashcards due *FRQ due *Download Ch. 8, 9, & 10 Study Guide and Reading Guides Wed II. KEEP IN MIND 1. You must MEMORIZE the cell structures and functions in Chapter 6. 2. You should ALWAYS do the Concept Checks at the end of each section in the textbook and the Self Quizzes at the end of the Chapter and check your answers. You will get higher test scores if you do this! Don’t forget to use the website (www.campbellbiology.com, too! There’s so much great stuff on there to help you learn! III. KEY VOCABULARY Chapter 6 magnification light microscope Scanning Electron Microscope organelles prokaryotic cells nucleoli endoplasmic reticulum ribosomes lysosomes mitochondria plastids cytoplasm grana microfilaments myosin microtubules basal bodies cilia resolving power Transmission Electron Microscope cell fractionation nucleus eukaryotic cells nuclear membrane cytosol Golgi apparatus peroxisomes intermembrane space chloroplasts thylakoids vacuoles actin cytoskeleton centrioles flagella endosymbiotic hypothesis IV. LEARNING TARGETS Chapter 6 6.1. For each of the organelles listed below, describe its structure; give a major function; indicate whether it is surrounded by a single membrane, a double membrane, or no membrane; and state whether it is found in plant, animal, or bacterial cells (a well-designed table is acceptable). nucleus nucleolus endoplasmic reticulum ribosome mitochondria lysosome plastids vacuole microtubules microfilaments Golgi apparatus centriole basal bodies cilia and flagella 6.2. Discuss four differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (Hint: see table 27.2) 6.3. Describe the endosymbiotic hypothesis for the origin of the eukaryotic cells and give three lines of evidence for the validity of this hypothesis. (Hint: see pages 523-525) 6.4. Describe the components of the "endomembrane system.” List one example of how these components function together as a unit. 6.5. Describe the structure and role of the cytoskeleton. 6.6. Describe the structure of cilia and flagella and how these structures allow for cell movement. 6.7. Describe the various types of cell junctions in both plant and animal cells. V. KEY VOCABULARY Chapter 7 diffusion selectively permeable osmotic potential hypotonic plasma membrane permease facilitated diffusion electrochemical gradient membrane pump sodium-potassium pump phagocytosis pseudopodia water potential osmosis osmotic concentration hypertonic isotonic fluid-mosaic model membrane channel electrostatic gradient receptor active transport endocytosis pinocytosis exocytosis VI. LEARNING TARGETS Chapter 7 7.1. Describe the process of osmosis and explain the relationship between osmosis and diffusion. How is the net movement of water through a membrane in osmosis related to the concentration of solute molecules? 7.2. Define the terms hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic. Explain what would happen to an animal cell and a plant cell placed in a hypertonic medium and to an animal cell and a plant cell placed in a hypotonic medium. 7.3. Construct a diagram and describe the fluid-mosaic model of the cell membrane. In your description, point out the phospholipid molecules, and indicate the hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions; point out the proteins that span the interior of the membrane and those that are confined to the surface; indicate the role of the cholesterol molecules, and explain why lateral movement of molecules within the membrane is possible. List substances to which the membrane is relatively permeable, and those to which it is relatively impermeable. 7.4. Describe the role that proteins (permeases) play in moving material through membranes. 7.5. Construct a diagram and explain how an electrochemical gradient can be generated across a membrane and what is meant by an electrochemical gradient. 7.6. Distinguish between simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and active transport. Indicate the role of these processes in the life of the cell. 7.7. Using diagrams, describe the processes of endocytosis, phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and exocytosis, explaining the role of these processes in transporting substances into and out of the cell. 7.8. Explain the concept of water potential and its importance to plant cells. 7.9. Read pages 92 & 93, “An Interview with Peter Agre.” What was his discovery and what does it have to do with the subject matter of Chapter 7?