* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
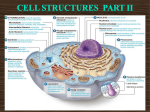
Download Structures found in Eukaryotes Continued 4. • Formed by • Vesicles
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Structures found in Eukaryotes Continued 4. • Formed by • Vesicles, including l_______________________ (digestive enzymes) and • peroxisomes (detoxification enzymes), are classified by their contents. Protein Synthesis – The rough ER, Golgi apparatus, and vesicles work together to transport _____________________ to their destinations inside and outside the cell. 5. -harvest __________________from organic compounds and transfer it to________. • • Has _______ membranes • -outer membrane (smooth) serves as a boundary • -inner membrane – Has many folds (_____________) to increase surface area – Cell respiration takes place Have their own DNA called ______________ Found in large # in cells that require energy. 6. • is made of ____________________ that help cells move and maintain their shape. • The cytoskeleton includes ___________________ (thin, hollow cylinders), __________________(thin, and solid cylinder), and intermediate filaments. • – Cilia and flagella are hairlike structures that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in movement. – Cilia-short; usually _____________ numbers – Flagella-longer whip-like; single or pair Structure “ _________________” microtubules • – consist of two short cylinders of microtubules at right angles to each other and are involved in cell division. (Not in plants) 7. -stores enzymes and waste products PLANT CELLS * • In plant cells, a rigid cell wall covers the cell membrane and provides __________ and ______________________. • Made of _________________ • Has pores, but is _________ selectively permeable Large ______________________store water, enzymes, and waste products and provide support for plant tissue. • In mature plants, can take up to ______of the volume of the cell.