* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download III - Humble ISD
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
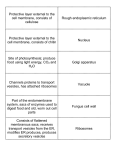
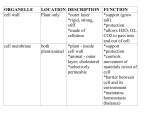
III. INSIDE A EUKARYOTIC CELL Cell Structure 1. a. b. c. 2. a. b. Function/Description Control center of eukaryotic cell a. Double membrane that protects nucleus; continuous with ER, contains pores to allow RNA to leave nucleus b. Site of ribosome and rRNA production c. Contains genes, composed of a complex DNA and protein called chromatin Network of membranous sacs and tubes extending though the cytoplasm 4. a. Site of lipid synthesis, detoxification of poisons, storage of Ca2+ ions, breakdown of glycogen in animals b. Name refers to presence of ribosomes; Site of secretory protein production (proteins destined for outside the cell) and additional membrane production. Proteins packaged in transport bubbles called vesicles. “Cell postmaster”; Receives transport vesicles from ER; modifies, stores, and ships products. The “receiving side” is known as the cis face; shipping side is known as the trans face. Suspended in cytosol or found on rough ER; site of protein production in a cell 5. Sacs containing hydrolytic enzymes; used for recycling cellular materials, destroying pathogens, absent in plants 6. Storage sac. In plants typically have large, central vacuole surrounded by membrane called tonoplast. Absorbs water and helps plant cell to grow larger. Some protists have contractile vacuole to pump out excess water. Type of plastid that carries out photosynthesis by converting solar energy to chemical energy (glucose). Contain membranous system of flattened sacs called thylakoids – stack is called a granum. Fluid surrounding thylakoids is called stroma – contains DNA ribosomes, enzymes. Site of oxidative respiration where glucose is converted into cellular energy (ATP). Contain own DNA, ribosomes. Enclosed by 2 membranes – inner membrane has folds called cristae to increase surface area. Membrane-bound compartments that use oxygen to carry out metabolism; forms H2O2 which is then broken down by enzymes 3. 7. 8. 9. 10. a. 11. Composed of proteins - Provides structural support to cell; more extensive in animal cells a. A.K.A. = actin filaments – thinnest filaments. Forms 3-d network that helps support cell shape, bear tension. Bundles of them form microvilli, extensions of the cell membrane found in some cells to increase surface area. Interact with myosin in muscle cells to create movement b. In between in thickness; more permanent than microtubules/filaments. c. Hollow rods – support cell, serve as tracks for movement within cell. Also help separate chromosomes during cell division - occurs in a region called centrosome, which is the location of centrioles in animal cells. Cilia and flagella – structures for movement found in some cells. Constructed from bundles of microtubules covered by extensions of the cell membrane. Encloses the cell, regulates materials in and out of the cell, helps maintain cell shape 12. Used for cell movement in sperm cells and in some other unicellular organisms 13. Multiple short projections extending from the cell surface which are used for movement 14. Pair of hollow cylinders in which the mitotic spindle forms between during cell division, absent in most plants b. c.