* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells_and_Chemical_Changes_Background_Info_
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
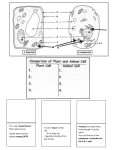
Cells and Chemical Changes Background Informataion Cells differentiate in both plants and animals. Although the groups of cells that form muscle tissue are different from the groups that form bone or blood, and cells that form roots of plants are different from those that form leaves. The protoplasm for all living cells in the human body comes from the foods people eat. How well cells work, how much energy a person has, and how an individual grows all depend on how food is selected, prepared, ingested, and digested. All plants and animals grow by reproducing cells. In large organisms such as people, the billions of cells perform many different roles. The cells combine to form body tissue and several different tissues also combine to form organs and to function as various parts of the body, from the brain to the big toe. Other forms of life such as microorganisms are made up of a very few cells or even one single cell and are also capable of carrying on all of life's processes. A basic understanding of cell structure and function is important to understanding how food functions in and for the human body. It is also essential to understanding the actions of bacteria, yeasts, and molds. Since the cell is the basic unit of all living things, you might think it is a simple structure. Nothing could be farther from the truth. The cell is complex in its makeup and its function. Many scientists have spent their lives studying it. Even with all of our advanced knowledge scientists are not yet able to explain how cells differentiate to become skin, muscle, nerves,etc. The main parts of any cell are the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell wall. In plants, the cell walls are thick and rigid. Animal cell walls are thinner and more pliable. (See transparency COMPOSITE PLANT AND ANIMAL CELL.) The nucleus of the cell is the control center. It directs cell division or the formation of new cells. The cytoplasm contains the parts which convert food material into energy and new cell material. The cell wall or membrane holds everything together and controls the passage of material into and out of the cell. Cells are remarkably diverse. Cells are never formed by nonliving things. They are found in nonliving matter (such as wood) only if it were once alive. Why are cell so small? Every bit of food and information (stimuli) needed by a cell must enter through the cell membrane. When cells are small, no part of their complex machinery lies too far from the area outside the cell. If a cell were larger, fewer of its interior structures could be near the cell membrane. Cells perform better if supply lines are short and cannot be cut off. Multicellular organisms, like humans, grow as their cells grow and divide. When cells reach a certain size, they stop growing or they divide to keep all parts of a cell very close together. As it grows, a cell's volume increases faster than its surface area (see transparency RATIO OF SURFACE AREA TO VOLUME IN CELLS.) As it takes in more nutrients, the cell grows, and it creates more wastes. The membrane has to accommodate the cells needs, but the membranes also limits cell growth because the surface of the cell is less than the volume. The volume cannot grow faster than the surface area of the membrane, because the surface area of the membrane allows food in and eliminates wastes. Cells and Chemical Reactions We are familiar with chemical reactions in test tubes, but chemical reactions associated with life processes, also take place in living cells. A chemical reaction is a process making or breaking chemical bonds. In plant cells, for example, light energy forms chemical bonds of molecules in large chains of glucose (sugar). Substances with more than one kind of atom are called compounds. Atoms in compounds are always in definite ratios. For example, oxygen is a substance that is classified as an element. Hydrogen is also an element because its atoms are of one kind. Water, however, is a compound because it contains hydrogen atoms and oxygen atoms, and they are always in the definite ratio of 2 hydrogens to one oxygen. Because atoms in compounds occur in definite ratios, scientists can write chemical formulas for substances, such as 1120 for water. Chemists can also classify substances into two broad groups: organic and inorganic. With few exceptions, organic substances contain the element carbon. Inorganic substances are elements other than carbon and compounds are elements with carbon. The categories are for convenience. Foods contain carbon, so does the human body. So, the study of foods and nutrition is considered to be based, among other things, upon organic chemistry. Substances undergo changes when their conditions are changed. A change in condition could be an increase in temperature, a mechanical deformation, exposure to another substance, or any number of other alterations. NOTE: If the same substance remains after the change, a physical change has taken plain. If popping of popcorn is reviewed, students can see it was a physical change. Whenever matter undergoes a change and a new substance with new characteristics is formed, a chemical change has taken place. Chemical changes often form compounds. For example, sodium is a soft, silvery metal that reacts with water. Chlorine is a yellow-green, corrosive, poisonous gas. If the two are brought together they will form a white crystalline solid that does not chemically react with water and is not poisonous. It is called sodium chloride. We know it as table salt. Chemical properties of a substance describe and are concerned with how a material will react with another material. Decomposing compounds into elements involves chemical properties. Burning, digesting, and fermenting are examples of chemical changes that decompose elements into compounds. Enzymes start many chemical reactions. Enzymes are made in living cells, and they start reactions but are not used up in the reaction. It is sort of like a spark plug causing a gasoline engine to ignite. Enzymes are also responsible for some extremely undesirable changes in food. Enzymes can cause both positive and negative reactions. They often cause fruits and vegetables to turn brown or gray. To inactivate enzymes, food can be briefly immersed in boiling water and then dried or frozen. Enzymes in food are also inactivated when oxygen is excluded, sulfur dioxide is used, or the pH is lowered. Enzymes are catalysts in the chemical process. Different kinds of enzymes are and can be produced in cells found in any living entity. They are proteinaceous substances produced by living cells. Catalysts make a reaction go faster. A common example of a catalyst is an enzyme in cells of an avocado speeding up the rate at which oxygen can combine with smashed avocado cells and turn guacamole brown. Enzymes, like microorganisms, can help or hinder food preparation and use of food in the body. Sometimes enzymes are beneficial; sometimes they are not. You will remember browning can be a problem in food preservation. Most browning in fruits and vegetables is caused by enzymes. On the other hand, enzymes made in the cells of the human body are essential to human health and well-being. Examples of enzymes causing chemical reactions: Enzymes Oxidation: fire, cooking, gasoline meat cooking fruit darkening The importance of remembering that the cell is the basic structure of all living things helps one understand what causes a number of problems and poses solutions in food preparation and utilization. Many chemical changes take place within the cells of living things.